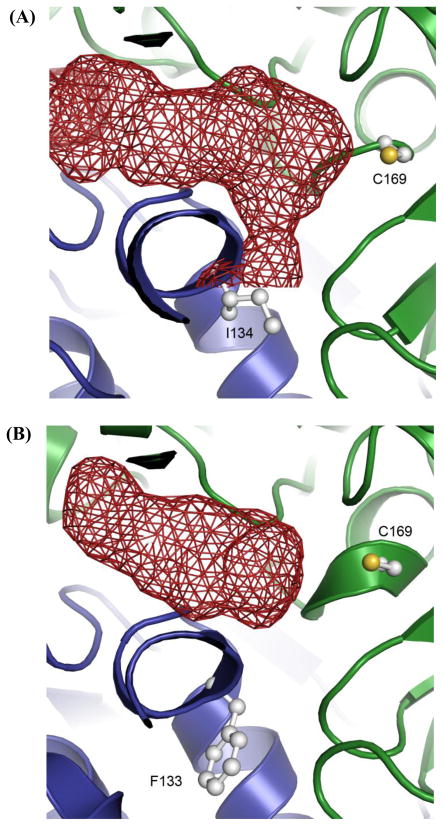
Figure 5.
Homology model of the fdm KS-CLF (A) along with the structurally characterized act KS-CLF (B). The KS and CLF subunits are shown as green and blue ribbons, respectively. The active site of the KS (C169) and residue 134 of the fdm CLF (F133 is an equivalent residue in the act CLF) are shown in balls and sticks. Polyketide chain growth is initiated via decarboxylation of malonyl-ACP, followed by transfer of the resultant acetyl group onto C169 residue of the KS. The growing polyketide chain is transferred back and forth between and Cys169 residue of the KS and the pantetheinyl thiol of the ACP until it reaches full length. At this point the chain fully occupies the substrate-binding channel (shown in red), and is subsequently released.