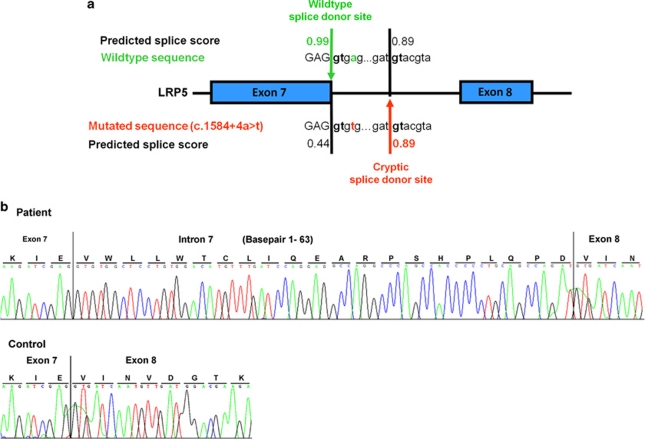
Figure 2.
Identification of the c.1584+4A>T disease-causing splice-site mutation in LRP5. (a) Direct-sequencing results of genomic DNA amplicons of the LRP5 exon 7 splice donor site in a control individual (wild-type sequence) and patient 3A (mutated sequence). The predicted splice score (0.99) of the wild-type splice donor site decreases to 0.44 in the mutated sequence, inducing the activation of a cryptic splice donor site downstream. (b) Electropherograms of LRP5 cDNA amplicons from patient 3A (upper panel) and a control individual (lower panel) revealing a mutated splice donor site after exon 7, with 63 additional nucleotides of intron 7 inserted into the RNA molecule in the patient's sample. The wild-type sequence is correctly spliced in the control individual.