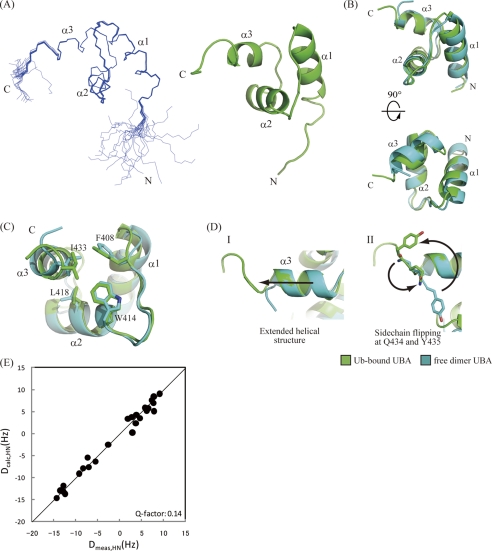
FIGURE 4.
NMR structure of p62 UBA domain in its ubiquitin-bound form. A, ensemble of the 20 lowest energy structures of the p62 UBA domain determined in a 6-equimolar amount of ubiquitin (left) and ribbon diagram of the energy-minimized averaged structure generated from the ensemble (right). B, superposition of the free-form crystal structure and the bound-form NMR structure of the p62 UBA domain. C, dimerization interface residues in both free- and bound-form structures of the p62 UBA domain are shown as stick models. D, structural comparison of the C terminus of the helix-3 between the free and the bound forms of the p62 UBA domain. The p62 UBA structure in its ubiquitin-bound form (NMR structure) is shown in green, and the free form (crystal structure) is shown in cyan. E, plot of calculated RDC constants of the free-form p62 UBA crystal structure (vertical axis) and measured RDC constants from the ubiquitin-bound p62 UBA sample (horizontal axis).