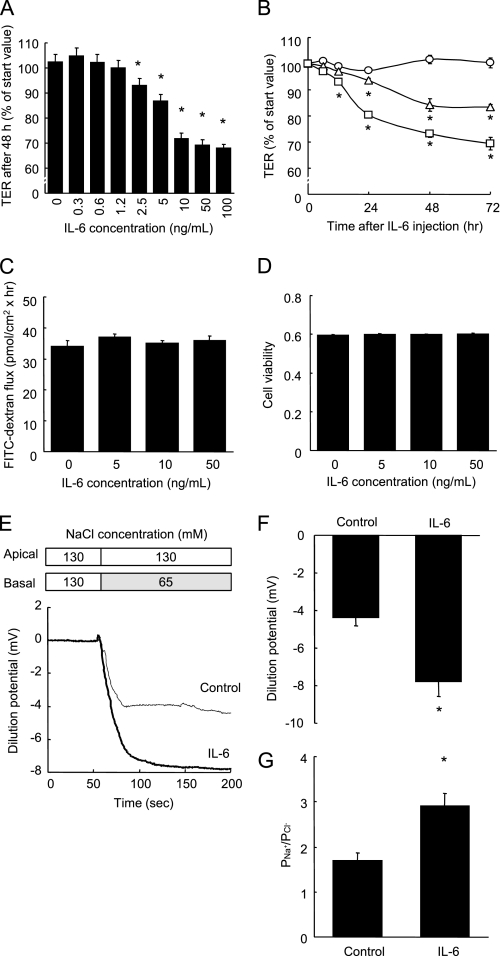
FIGURE 1.
IL-6 increases TJ permeability to ionic solutes without any changes to dextran flux or cell viability. A, TER was measured across Caco-2 cell monolayers incubated with varying concentrations of IL-6 (0∼100 ng/ml) for 48 h. *, p < 0.05 relative to the control value. B, TER was measured across cell monolayers before incubation and 3, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h after incubation with IL-6 (0, 5, and 10 ng/ml). *, p < 0.05 relative to the control value at each time point. C and D, unidirectional FITC-dextran flux (C) was evaluated across Caco-2 cell monolayers incubated with varying concentrations of IL-6 (0∼50 ng/ml) for 48 h, and cell viability was assessed by WST assay (D). E–G, NaCl dilution potentials were measured across Caco-2 cell monolayers incubated with or without 10 ng/ml IL-6 for 48 h by the basal substitution of 65 mm NaCl with 130 mm mannitol. Representative electrophysiologic measurements (D), the statistical analysis of the dilution potentials, and PNa+/PCl− calculated from stable dilution potentials (G) are shown. *, p < 0.05 relative to the control value. Values represent the mean ± S.E. (n = 6).