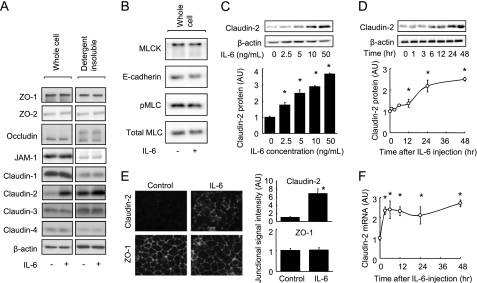
FIGURE 2.
IL-6 induces claudin-2 expression in Caco-2 cells. A, whole cell extracts and detergent-insoluble fractions of Caco-2 cell monolayers incubated in the absence or presence of IL-6 (10 ng/ml) for 48 h were immunoblotted for ZO-1, ZO-2, occludin, JAM-1, claudin-1, claudin-2, claudin-3, claudin-4, and β-actin. B, whole cell extracts of Caco-2 cell monolayers incubated in the absence or presence of IL-6 (10 ng/ml) for 48 h were immunoblotted for MLCK, E-cadherin, pMLC, and total MLC. C, whole cell extracts of Caco-2 cell monolayers incubated with varying concentrations of IL-6 (0∼50 ng/ml) for 48 h were immunoblotted for claudin-2 and β-actin. Specific bands for claudin-2 were quantitated by densitometric analysis. D, whole cell extracts of Caco-2 cell monolayers before and 1, 3, 6, 12, 24, 48 h after incubation with IL-6 (10 ng/ml) were immunoblotted for claudin-2 and β-actin. Specific bands for claudin-2 were quantitated by densitometric analysis. E, Caco-2 cell monolayers incubated in the absence or presence of IL-6 (10 ng/ml) for 48 h were immunolabeled for claudin-2 and ZO-1. The fluorescent signal intensity of claudin-2 and ZO-1 in the junctional region of cells was quantified. F, claudin-2 mRNA expression was analyzed by qPCR in cell monolayers before incubation and 3, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h after incubation with IL-6 (10 ng/ml). *, p < 0.05 relative to the control value (IL-6-free or pretreatment levels). Values represent the mean ± S.E. (n = 4).