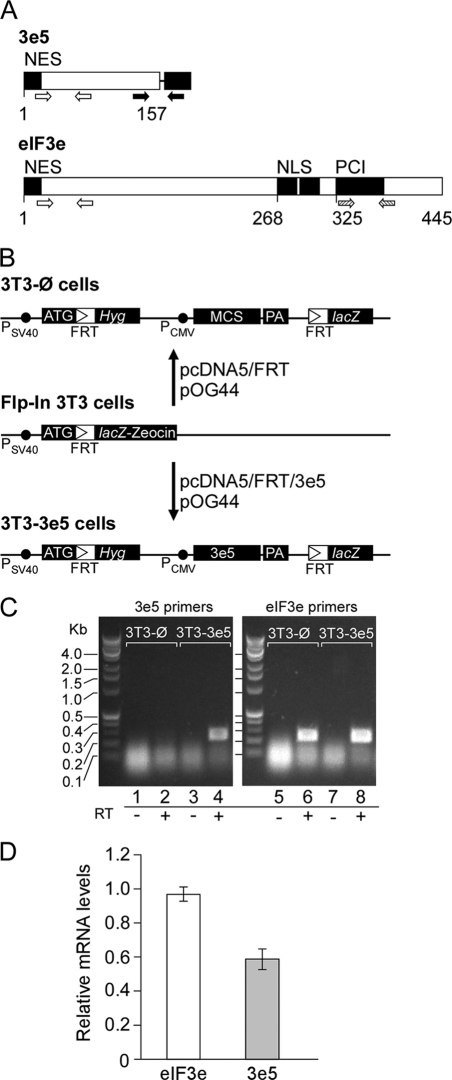
FIGURE 1.
Construction of NIH3T3 cells expressing 3e5. A, 3e5 and full-length eIF3e. The mRNA produced by insertion of MMTV at intron 5 of the Eif3e gene encodes eIF3e truncated after 157 amino acid residues (3e5) whereas the full-length protein contains 445 amino acid residues. The black box to the right of 3e5 represents vector sequences. Open arrows show positions of primer set 8 on the corresponding mRNA, which amplifies sequences in both 3e5 and Eif3e. Solid arrows show positions of primer set 6, which amplifies sequences only in 3e5 because the reverse primer is complementary to vector sequences. Cross-hatched arrows show positions of primer set 7, which amplifies sequences only in Eif3e. NES, nuclear export signal. NLS, nuclear localization signal. PCI, the 26 S proteasome-COP9 signalosome-eIF3 domain. B, construction of 3T3-Ø and 3T3–3e5 cells. Insertion of 3e5 and vector sequences by homologous recombination. C, detection of 3e5 and Eif3e mRNAs by RT-PCR. RNA extracted from 3T3-Ø and 3T3–3e5 cells was subjected to PCR with either 3e5-specific primers (primer set 6; lanes 1–4) or Eif3e-specific primers (primer set 7; lanes 6–8). Reverse transcriptase was omitted in lanes 1, 3, 5, and 7. D, relative mRNA levels of 3e5 and endogenous Eif3e mRNA levels were quantitated as described under “Experimental Procedures” for four independent experiments.