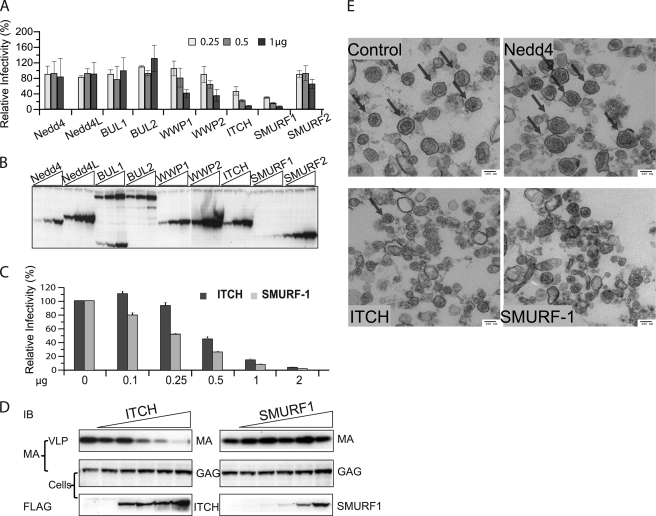
FIGURE 2.
Overexpression of ITCH and SMURF-1 reduces the infectivity and release of HTLV-1 wt. A, relative infectivity of HTLV-1 VLPs in the presence of different ULs. 3 × 105 293T cells were transfected with 0.2 μg of pCMVHT-1MΔenv, 0.3 μg of pCRU5inGlucβ, and 0.03 μg of pCMV-VSV-G and three different concentrations (0.25, 0.5, and 1 μg) of plasmids encoding FLAG-tagged Nedd4 family ULs. The infectivity of the VLPs was determined by measuring the Gluc activity in the supernatant 48 h after transfection. The infectivity of HTLV-1 wt VLPs without exogenous UL was set as 100%. The data represent the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. B, representative anti-FLAG immunoblot of cell extracts used in the experiment in A showing the expression levels of the different ULs. C, the infectivity of wt HTLV-1 is reduced in the presence of increasing amounts of ITCH and SMURF-1. 293T cells were transfected with the retroviral vectors constructs as in A and 0, 0.1, 0.25, 0.05, 1, or 2 μg of pCI-FLAG ITCH or pCI-FLAG SMURF-1. The infectivity of the VLPs was determined by measuring Gluc activity in the supernatants 48 h after transfection. The data represent the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. D, the overexpression of ITCH, but not SMURF-1, inhibits release of HTLV-1 wt. Immunoblot analysis of pelleted virus particle and cell lysates of transfected cultures generated in D using the indicated antibodies. E, ITCH and SMURF-1 impact the quantity and quality of HTLV-1 wt virus particles. Representative TEM images of HTLV-1 wt VLP pellets produced in by co-transfection of 5 × 106 293T cells with 5 μg of pCMVHT-1MΔenv and 10 μg of pCI-FLAG-Nedd4, -ITCH, or -SMURF-1. Arrows indicate particles with HTLV-1 wt morphology.