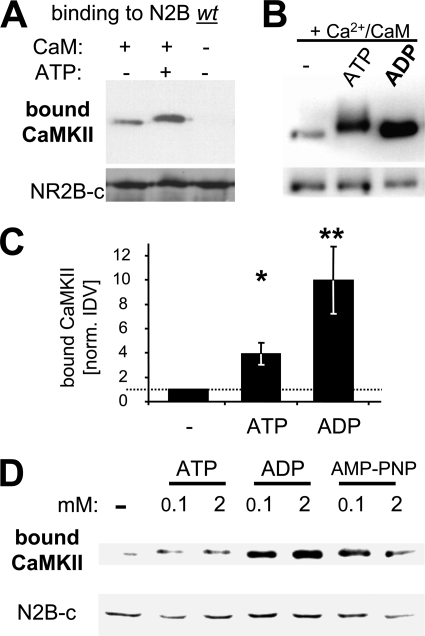
FIGURE 2.
ATP and other nucleotides enhance Ca2+/CaM-induced CaMKII binding to GluN2B. A, addition of ATP (100 μm) enhanced Ca2+/CaM-induced CaMKII binding to GluN2B in vitro, as determined by Western blot analysis of the protein complex. B, addition of ADP (100 μm) enhanced Ca2+/CaM-induced CaMKII binding to GluN2B even more than ATP (without the slight band shift caused by autophosphorylation in presence of ATP). C, quantification of experiments as shown in panels A and B (n = 6; for ADP n = 3)). The significantly increased CaMKII binding in presence of ATP (*, p < 0.05) was significantly further increased when ADP was present instead (**, p < 0.01; in Neuman-Keuls multiple comparison test, after one-way ANOVA). Error bars show S.E. D, increasing the amount of nucleotide (ATP, ADP, or AMP-PNP) from 100 μm to 2 mm did not increase CaMKII binding to GluN2B any further, as determined by Western blot analysis.