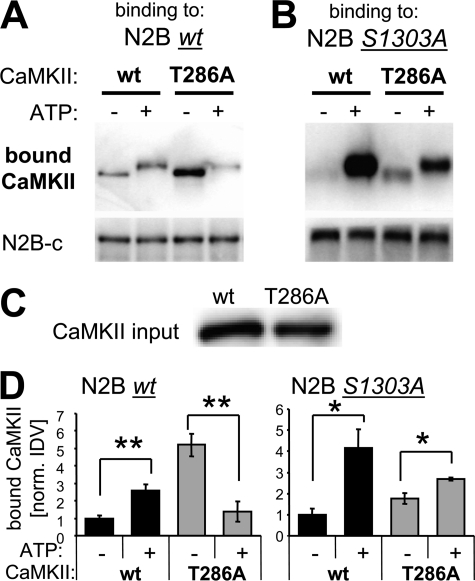
FIGURE 4.
ATP enhances CaMKII binding to GluN2B, directly and by inducing T286 autophosphorylation. GFP-CaMKII purified after over-expression in HEK 293 cells was used for these binding experiments. A, increase in CaMKII binding to GluN2B wild type caused by ATP was not only abolished but even reversed for the CaMKII T286A mutant, as determined by Western blot analysis of the protein complex. B, an increase in CaMKII binding to GluN2B S1303 caused by ATP was also seen for the CaMKII T286A mutant, but to a lesser extent than for CaMKII wild type. C, similar amounts of GFP-CaMKII wild type and T286A mutant were used in the binding experiments, as determined by Western blot analysis of the input mix of the binding reaction. D, quantification of experiments as shown in panels A (n = 4) and B (n = 3). Binding to GluN2B wild type was significantly enhanced by ATP for CaMKII wild type, but significantly reduced for CaMKII T286A (**, p < 0.005; t test). By contrast, binding to GluN2B S1303A was enhanced by ATP for both CaMKII wild type and the T286A mutant (*, p < 0.05; t test). Error bars show S.E.