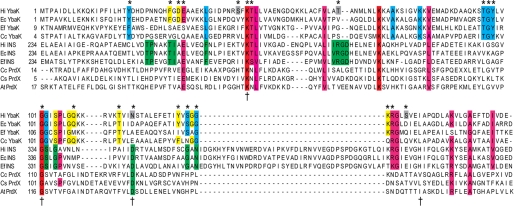
FIGURE 1.
Multiple-sequence alignment of YbaK superfamily. Multiple-sequence alignment of members of the YbaK superfamily performed using the ClustalW multiple-sequence realignment program (45). The alignment of YbaK, INS domain of prokaryotic-like ProRS, and PrdX is shown. Functionally important residues in E. coli ProRS for editing are indicated by a dagger (42). The residues in H. influenzae YbaK investigated by mutagenesis in this study are indicated by an asterisk. Residues are colored as follows. Red, strictly conserved in YbaK, INS, and PrdX; pink, highly conserved in YbaK/INS; green, highly conserved in INS; blue, highly conserved in YbaK; yellow, partially conserved in YbaK; gray, not conserved but selected for mutagenesis. Ec, E. coli; Hi, H. influenzae; Ef, E. faecalis V583; Cc, Caulobacter crescentus CB15; At, Agrobacterium tumefaciens.