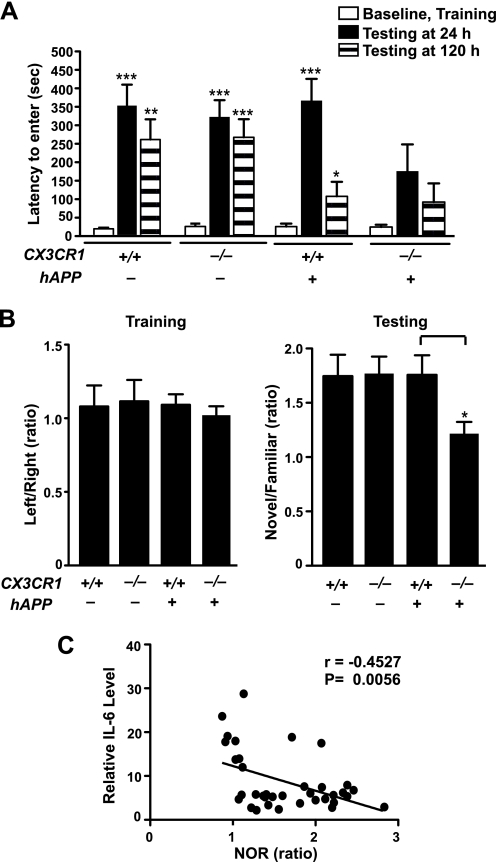
FIGURE 5.
CX3CR1 ablation exacerbates cognitive deficits in hAPP mice. A, in the passive avoidance task, the increased escape latency to enter the dark chamber during the test indicates memory retention. No difference was detected during the training (Baseline). During the test performed 24 or 120 h after the shock, latency was significantly increased in CX3CR1+/+, hAPP/CX3CR1+/+, and CX3CR1−/− mice, but not in hAPP/CX3CR1−/− mice. hAPP/CX3CR1+/+ mice exhibited reduced latency 120 h after the training. n = 8–10/genotype, 3–8 months old. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001, paired Student's t test as compared with the correspondent training latency. Latency was recorded up to 500-s cutoff. B, in the novel object recognition task, the preference to the novel object, as measured by the ratios of the time spent on the novel versus familiar object during the test session, reflects memory retention. All genotypes exhibited no preference during the training session when left and right objects were the same. During the test session, hAPP/CX3CR1−/− mice exhibited less preference to the novel object than hAPP/CX3CR1+/+ mice. n = 8–10/genotype. *, p < 0.05, unpaired Student's t test. C, levels of IL-6 negatively correlated with the preference of the novel object recognition (NOR) test. n = 8–10 mice/genotype, Pearson's correlation. Values are means ± S.E. (A and B).