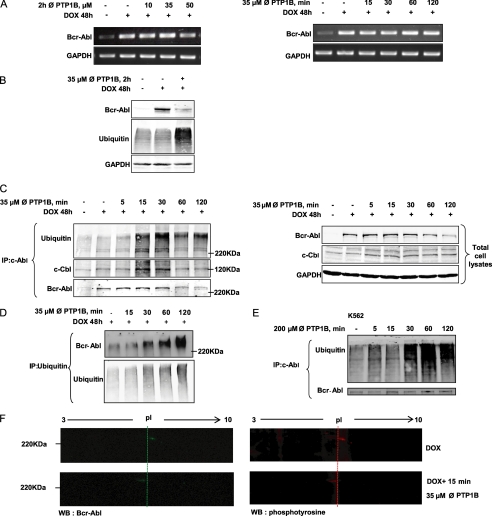
FIGURE 3.
Bcr-Abl is degraded at the protein level through the ubiquitin proteolytic system. A, RT-PCR analysis of Bcr-Abl mRNA extracted from the TonB.210 cells was carried out to examine the effect of different doses and times of PTP1B inhibition on transcription of the bcr-abl gene. GAPDH is shown as loading control. ∅, PTP1B, PTP1B inhibitor. B, TonB.210 cells were treated with 35 μm of the PTP1B inhibitor for 2 h, and the expression of Bcr-Abl and ubiquitin proteins in treated and untreated cells was determined by Western blotting. GAPDH was blotted as a protein-loading control. C, TonB.210 cells were treated with 35 μm of the PTP1B inhibitor for the indicated times. After this, c-Abl was immunoprecipitated (IP) from the cell lysates and immunoblotted with anti-c-Abl antibody, anti-c-Cbl antibody, or anti-ubiquitin antibody. Total cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to membranes, and subjected to immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. GAPDH was used as a protein-loading control. Bcr-Abl was detected at predicted size. D, TonB.210 cells were treated with 35 μm of the PTP1B inhibitor for the indicated times. Immunoprecipitation of ubiquitin was followed by immunoblotting for Bcr-Abl and ubiquitin. E, K562 cells were treated with 200 μm PTP1B inhibitor for the indicated times. Following this, c-Abl was immunoprecipitated from the cell lysates and immunoblotted with anti-c-Abl antibody and anti-ubiquitin antibody. Bcr-Abl was detected at predicted size. F, TonB.210 cells, in presence of DOX, were left untreated or were treated for 15 min with 35 μm PTP1B inhibitor. Total cell lysates were resolved by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, transferred to membranes, and immunoblotted (WB) with anti-c-Abl antibody (green) or anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (red). The membranes were cropped to highlight the Bcr-Abl point shift. pl, isoelectric point.