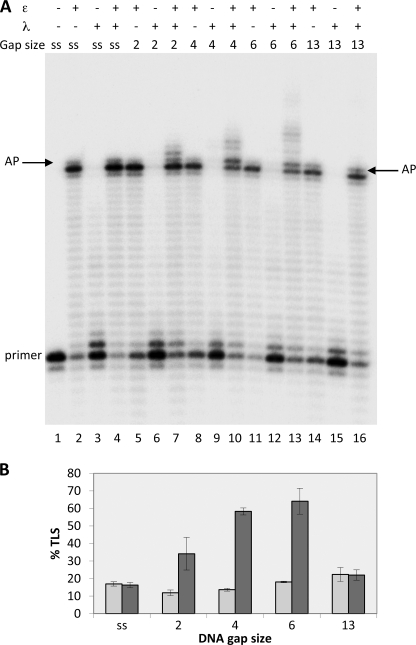
FIGURE 1.
Ability of DNA pol λ to perform translesion synthesis of an AP site in the presence of DNA pol ϵ depends on the gap size. Experiments were performed with templates shown in Table 1, part a. The enzymes and the DNA substrates used are indicated at the top. ss (single-stranded) stands for template-primer with no oligonucleotides hybridized downstream from the AP site; 2, 4, 6, and 13 indicate the length of gap regions between the AP site and the oligonucleotide hybridized downstream. Assays were carried out as described under “Experimental Procedures.” A, lane 1, no polymerase present. Lanes 2, 5, 8, 11, and 14, reactions incubated for 35 min with 0.025 pmol of pol ϵ. Lanes 3, 6, 9, 12, and 15, reactions incubated for 5 min with 0.25 pmol of pol λ. Lanes 4, 7, 10, 13, and 16, reactions were incubated with 0.025 pmol of pol ϵ for 30 min; then 0.25 pmol of pol λ were added, and incubation was continued for 5 min. The positions of the primer and of the AP site are indicated. B, quantification of the percentage of TLS calculated as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Mean ± S.D. values for three independent experiments are indicated. Light gray bars, pol ϵ alone. Dark gray bars, pols ϵ and λ together.