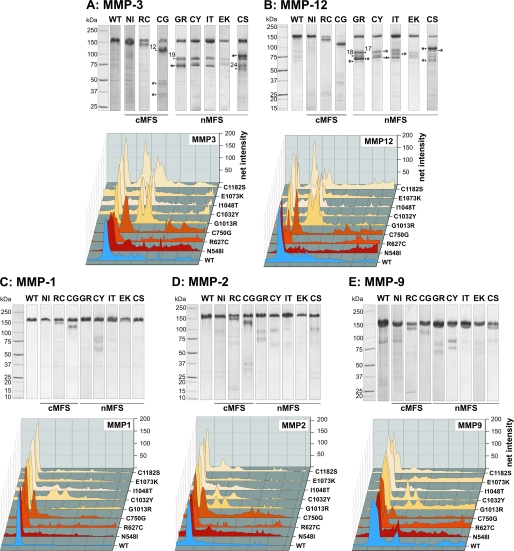
FIGURE 6.
Proteolysis of rF20 polypeptides by MMPs. 7 μg of each polypeptide was digested with MMP-3 (A), MMP-12 (B), MMP-1 (C), MMP-2 (D), and MMP-9 (E). Degradation products were separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (upper panels). The numbered arrows correlate with the determined N-terminal sequences of the degradation products summarized in Table 3. The abbreviations of mutations are used according to Table 1. Mutations leading to classical Marfan syndrome are indicated as cMFS, and mutations leading to neonatal Marfan syndrome are indicated as nMFS. Fragments with an N-terminal amino acid sequence of APLADYCQ (N terminus of rF20) are labeled with an asterisk (*). Each lane of the degradation analyses was analyzed by densitometry and plotted as a three-dimensional graph (lower panels). The profile of the WT is depicted in blue, the cMFS mutations is in shades of red, and the nMFS mutations are in shades of beige. High molecular weight bands are positioned on the left.