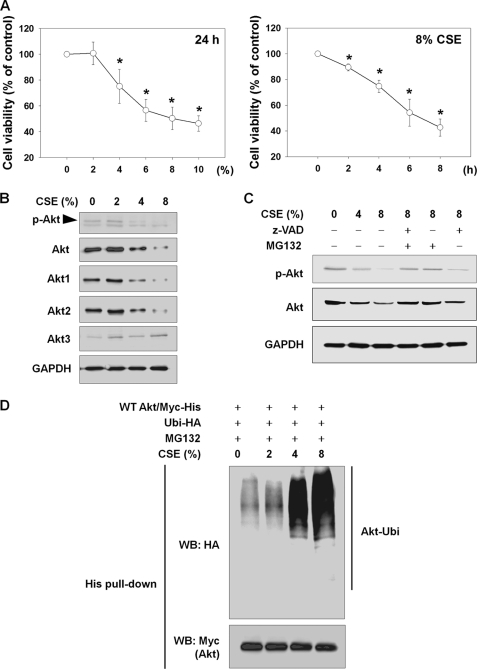
FIGURE 1.
CSE causes cell death and Akt degradation through the UPS in NHLFs. A, CSE-induced cytotoxicity. To determine concentration- or time-dependent cytotoxicity, NHLFs were exposed to the indicated concentrations of CSE for 24 h or to 8% CSE for the indicated times in the absence of serum. Cell viability was evaluated by an MTT assay. Data represent the means ± S.D. Asterisks denote a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) compared with the CSE-unexposed control. Number of each group is six. B, reduction in Akt and p-Akt by CSE exposure. After 24 h of CSE exposure, the reduction in total Akt, Akt1, Akt2, Akt3, and p-Akt (Ser-473) was assessed by Western blot. C, involvement of caspases and the proteasome in CSE-induced Akt reduction. NHLFs were exposed to CSE for 24 h. For the last 6 h, 10 μm Z-VAD or MG132 was added. D, Akt ubiquitination by CSE. NHLFs were transfected with the Myc-His-tagged wild-type Akt (WT Akt/Myc-His) and hemagglutinin-tagged ubiquitin (Ubi-HA) plasmids. After 24 h, NHLFs were exposed to CSE for another 24 h in serum-free DMEM with addition of 1 μm MG132 to prevent proteasomal degradation of ubiquitinated proteins. Ubiquitinated Akt was identified by His tag pulldown and Western blot (WB).