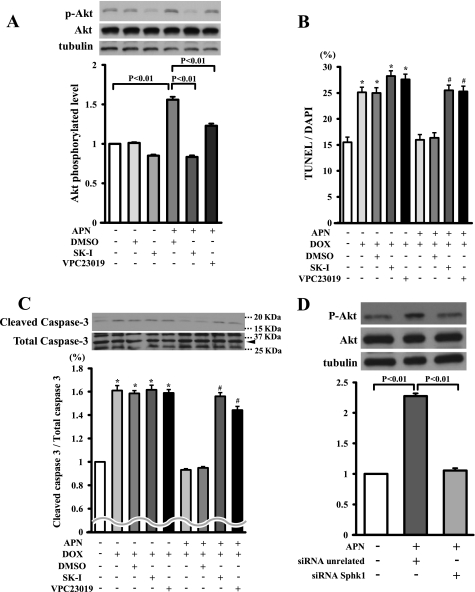
FIGURE 4.
SphK-dependent Akt signaling is essential for inhibitory effects of adiponectin on DOX-induced apoptosis. A, Western blot analysis for adiponectin-induced phosphorylation of Akt in the presence of the SphK-1 inhibitor, the S1P receptor antagonist VPC23019, or vehicle (DMSO). Quantitative analysis of relative changes in phosphorylated Akt (P-Akt) is shown. Phosphorylation of Akt was normalized to the α-tubulin signal (n = 4 in each group). B and C, effect of SphK-1 inhibitor or VPC23019 on the inhibitory effects of adiponectin on DOX-induced myocyte apoptosis. Cells were pretreated with SphK-1 inhibitor, VPC23019, or vehicle (DMSO) for 60 min and treated with or without adiponectin (10 μg/ml) for 24 h. Quantitative analysis of TUNEL-positive nuclei (B) and caspase-3 activity (C) is shown. TUNEL-positive nuclei were counted in several randomly selected fields and expressed as a percentage of the total number of nuclei (n = 4). D, representative immunoblots of phosphorylated Akt following treatment with adiponectin for 16 h in the presence of siRNA targeting SphK-1 or unrelated siRNA in cardiac myocytes (top). Bottom, quantitative analysis of relative changes in phosphorylated Akt. SK-I, SphK-1 inhibitor. (*, p < 0.05 versus control; #, p < 0.05 versus APN+/DOX+/DMSO+/SK−I−/VPC23019−.)