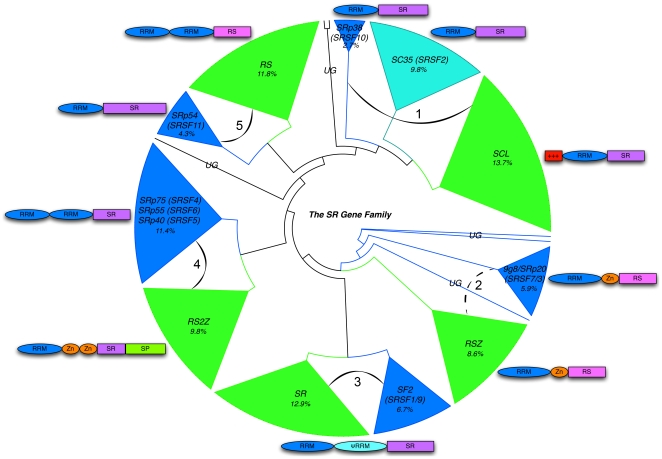
Figure 1. Condensed SR gene family tree.
Schematic representation (from FigTree [87]) of the sub-family relationships among 272 SR genes from the organisms sampled in this study. The numbered curved lines indicate the major groupings. Domain organization is presented adjacent to each clade. Green clades represent plant-enriched or plant-specific sub-families, whereas blue clades represent non-photosynthetic organisms. The turquoise SC35 clade denotes the mixture of plant SC members and non-plant SRSF2 members. The sum of these clades will yield 11 distinct sub-families. Taxa grouped into plant-enriched families that are non-photosynthetic are indicated in red. Species prefixes are as follows: Gm, Glycine max; Pt, Populus trichocarpa; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Vv, Vitis vinifera; Zm, Zea mays; Sb, Sorgum bicolour; Os, Oryza sativa; Sm, Selaginella moellendorfii; Pp, Physchomitrella patens; Cr, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; Cv, Chlorella vulgaris; Cm, Cyanidioschyzon merolae; Hs, Homo sapiens; Mm, Mus musculus; Gg, Gallus gallus; Xt, Xenopus tropicalis; Dr, Danio rerio; Br, Branchiostoma floridae; Ci, Ciona intestinalis; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; Ag, Anopheles gambiae; Aa, Aedes aegyptii; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans; Nc, Sp, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Dd, Dictyostelium discoideum; Pf, Plasmodium falciparum; Ps, Phytopthora sojae. UG, ungrouped.