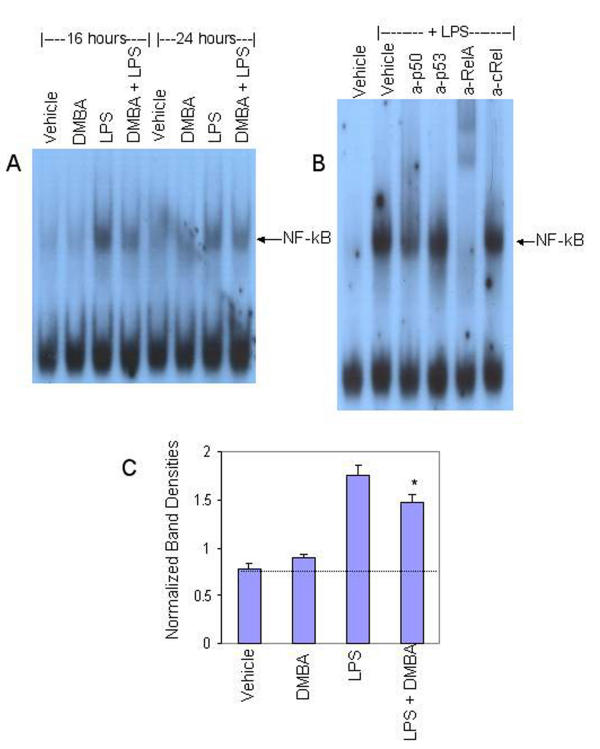
Figure 5.
DMBA inhibits LPS-induced NF-κB-DNA binding. BMS2 cells were left untreated (naïve) or were pre-treated with vehicle (0.01% ethanol) or 1 μM DMBA for one hour prior to challenge with 1 μg/ml LPS. Cells were harvested 16 and 24 hrs later. Nuclear proteins were extracted and analyzed by EMSA for binding to an NF-κB probe derived from the c-myc upstream regulatory element. (A) Data from a representative experiment (three total) are presented. An arrow indicates the NF-κB-specific band. (B) EMSAs were performed with nuclear extracts from BMS2 cells treated for 30 min with LPS in the presence of antibodies specific for the p50, p53, RelA (p65), or c-Rel subunits of NF-κB. (C) Quantification of NF-κB-DNA binding in nuclear extracts treated for 16–24 hrs. NF-κB band densities were normalized to untreated controls within the same experiments. **Significantly different from LPS-plus vehicle-treated control, p < 0.05 (paired t-test).