Figure 4.
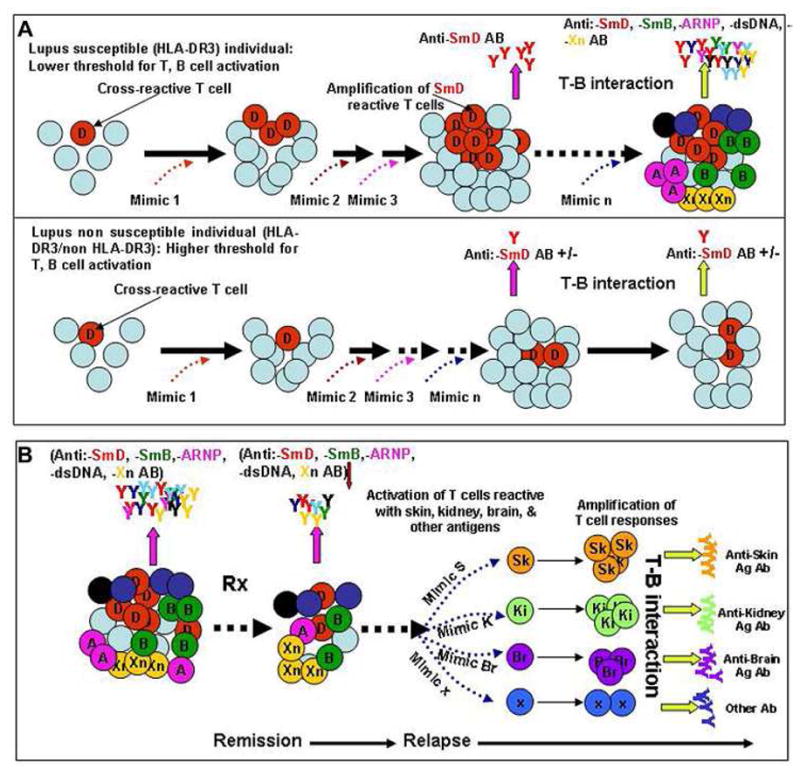
Generation of autoreactive Abs and effector T cells in SLE by environmental T cell epitope mimics. A. Accumulation of cross-reactive T cells as a consequence of response to environmental mimics in hosts (HLA-DR3+) with lupus susceptibility genes but not in hosts (HLA-DR3+) without these genes. B. The accumulation of diverse autoantibodies as a response to these mimics generates pathogenic autoreactive Abs and effector T cells. After therapy, the complexity of these autoantibodies and autoreactive T cells are reduced, leading to remission. Over a period of time after discontinuing therapy, the complexity of autoantibodies and effect T cells returns leading to a protean clinical presentation in relapses. The mimics reside on a diverse array of environmental antigens and the chances for exposure to these mimics are random, providing a scenario in that SLE is not caused by a single pathogen. This mechanism has the flavor of a stochastic process.
