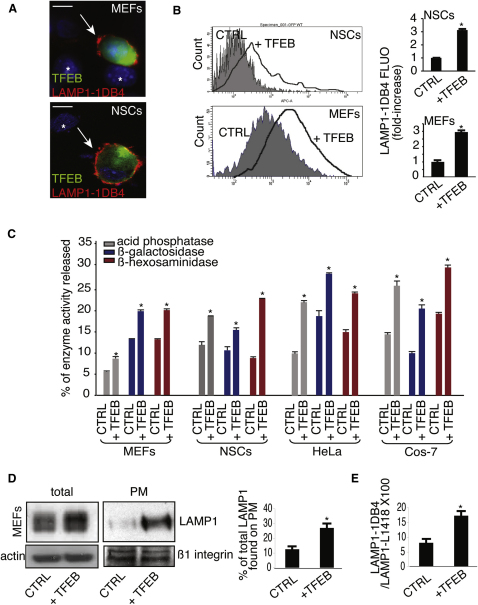
Figure 1.
TFEB Overexpression Induces Lysosomal Exocytosis
(A) Confocal microscopy images showing the exposure of LAMP1 on the PM in both nonpermeabilized NSC cells and MEFs transfected with either a bicystronic plasmid expressing TFEB-GFP or with an empty vector. LAMP1 was detected using an antibody against its luminal portion (LAMP1-1DB4). TFEB-transfected cells were localized by the expression of GFP; nontransfected cells are indicated by asterisks.
(B) Quantitative analysis by flow cytometry of LAMP1 levels on the PM in both NSCs and MEFs that express either a bi-cystronic TFEB-GFP plasmid or GFP. Bars represent the fold increase of LAMP1 fluorescence on PM in TFEB-transfected versus GFP-transfected (control) cells.
(C) TFEB overexpression increases the release of lysosomal enzymes in the culture medium of MEFs, NSCs, HeLa, and COS-7 cells. Activities of lysosomal enzymes acid phosphatase, β-galactosidase, and β-hexosaminidase were determined in the culture medium and in cells transfected with either an empty vector or with a TFEB-expression vector. The figure shows percentages of enzyme activities released compared with total activities.
(D) Representative immunoblots showing LAMP1 levels in both total lysates and enriched PM extracts from MEFs transfected with either TFEB or with an empty vector. Results were normalized using an antibody against actin and the PM protein β1-integrin, respectively. The histogram shows the quantification of LAMP1 detected by the immunoblot.
(E) Total and surface LAMP1 levels after TFEB overexpression were analyzed by flow cytometry analyses using the LAMP1-1DB4 and the LAMP1-L1418 antibodies that are able to detect PM- and intracellular-LAMP1, respectively. Data represent mean ± SEM; ∗p < 0.05 (B, C, D, and E). Scale bar represents 10 μm (A).