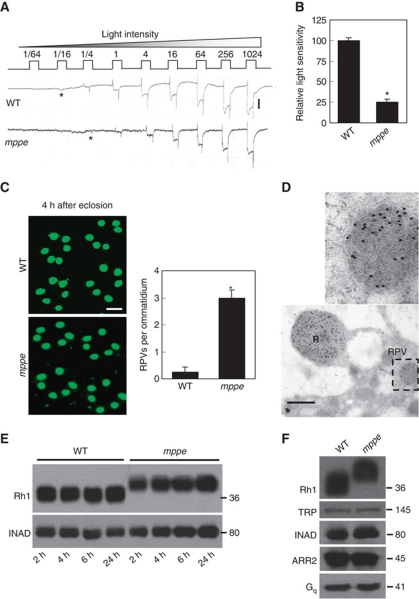
Figure 1.
Newly eclosed dmppe mutants show reduced light sensitivity, abnormal distribution and high molecular weight of Rh1. (A) ERG recordings revealed the reduction of light sensitivity in newly eclosed dmppe mutants. Flies were raised in the dark and examined within 4 h after eclosion. Fly eyes were stimulated with a series of 1 s light pulses of increasing intensities as labelled on the top. The first response appearing is marked with an asterisk. The scale bar next to the top trace is 5 mV. (B) Quantification of light sensitivities in newly eclosed flies. The mean relative sensitivities shown were calculated as described in Materials and methods. The error bar represents standard error of the mean (s.e.m.). *Indicates that the sample is significantly different from others in the group. (C) Rh1 distribution in the photoreceptors of newly eclosed flies. Cross-sections were prepared as described in Materials and methods. The sections were stained with a monoclonal Rh1 antibody (4C5). The number of RPVs per ommatidium was calculated for each genotype. Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) Immunogold electron microscopy reveals that RPV appeared to be the aggregation of small vesicles. Sections were prepared as described in Materials and methods. One RPV (boxed) is enlarged in the upper panel. Scale bar, 2 μm. (E) Reduction of Rh1 level in newly eclosed dmppe mutants. Flies were raised in the dark and heads were collected at the indicated time after eclosion. The scaffold protein INAD was probed in parallel. (F) Western blots show the increase in Rh1 MW in the mutant. The MWs of other visual molecules are normal. WT: wild type.