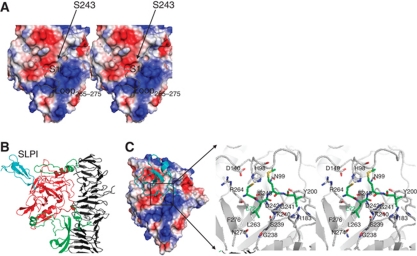
Figure 3.
Serine protease domain. (A) Molecular surface of the HapS serine protease domain reveals a V-shaped binding groove (indicated by dashed line). The active site loop265−275 (coloured in grey) is modelled based on the equivalent loop in the Hbp structure through structural superimposition. (B) Simulated complex of SLPI (cyan) bound to the HapS serine protease domain (red). The upper part of the helical spine and the protruding subdomains that mediate the orientation of the HapS serine protease domain are shown in cartoon diagram and coloured in grey and green, respectively. (C) Active site. Left panel: the serine protease domain is shown in electrostatic surface, and SLPI is shown in ribbon diagram (cyan). Right panel: close-up view of the active site. Simulated SLPI and surrounding residue from HapS are shown in stick and coloured in green and grey, respectively.