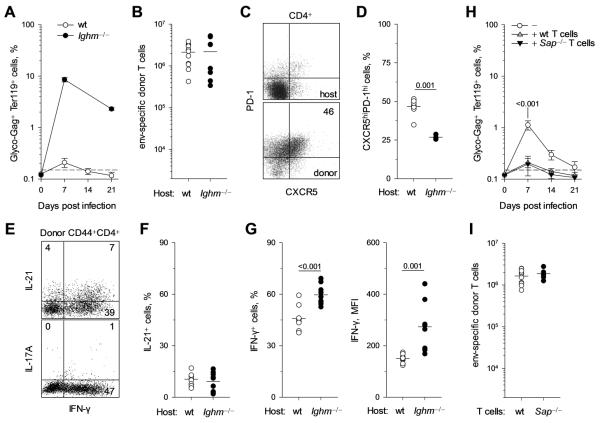
FIGURE 2.
Role of B cells in virus-specific CD4+ T-cell expansion and differentiation. (A-G). Cohorts of CD45.1+ TCRβ-transgenic CD4+ T cells were adoptively transferred into wt or B-cell-deficient Ighm−/− hosts and analyzed 7 days later. (A) Mean frequency (± SEM, n = 5-9) of FV-infected (glyco-Gag+) Ter119+ cells in the spleens of FV-infected wt or Ighm−/− hosts. (B) Absolute number of splenic env-specific donor (CD44hi CD45.1+) CD4+ T cells 7 days after transfer. (C) Example of CXCR5 and PD-1 expression in host or donor CD4+ T cells from wt hosts. (D) Frequency of CXCR5hiPD-1hi cells in env-specific donor CD4+ T cells from wt or Ighm−/− hosts. (E) Example of IFN-γ, IL-21 and IL-17A production by env-specific donor CD4+ T cells from wt hosts. (F, G) Frequency of IL-21+ cells (F) or IFN-γ+ cells (F, Left) and MFI of IFN-γ staining (F, Right) in env-specific donor CD4+ T cells from wt or Ighm−/− hosts. (H) Mean frequency (± SEM, n = 8-9) of FV-infected (glyco-Gag+) Ter119+ cells in the spleens of FV-infected wt hosts that received no T cells (−), in comparison with those that received wt (+ wt T cells) or Sh2d1a−/− (+ Sap−/− T cells) TCRβ-transgenic env-specific CD4+ T cells. (I) Absolute number of either wt (+ wt T cells) or Sh2d1a−/− (+ Sap−/− T cells) splenic env-specific donor (CD44hi CD45.1+) CD4+ T cells 7 days after transfer into FV-infected wt hosts. In B, D, F, G and I, each symbol is an individual mouse.