Figure 1.
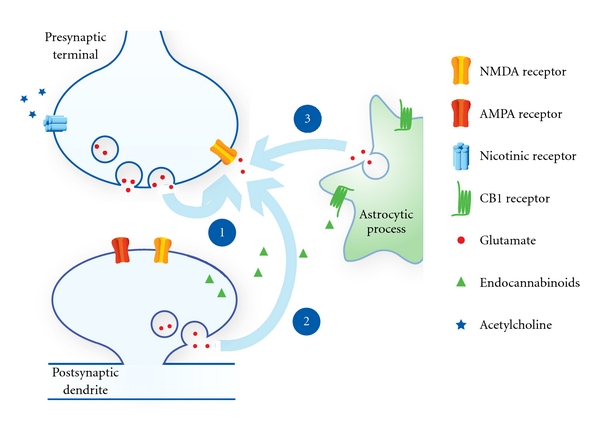
Three possible sources of glutamate for preNMDAR activation. (1) The first and most straightforward route would be that preNMDARs are auto-receptors that receive glutamate from the same terminals on which they are located. A problem with this scenario is that the necessary depolarisation for NMDAR activation may have ended by the time glutamate has reached the receptor. Therefore, preNMDARs will either need to be less voltage-sensitive or require some other source of depolarisation. (2) A second possibility is that glutamate derives from the postsynaptic cell. In a post-before-pre pairing protocol, the depolarisation of the postsynaptic neuron can elicit glutamate release which will activate preNMDARs when these are depolarised by the presynaptic action potential. (3) eCBs, released postsynaptically following depolarisation, can act on CB1Rs on nearby astrocytes to induce astrocytic glutamate release. The question is whether this mode of glutamate delivery will be fast enough to play a role in the tLTD induced at small pairing intervals in the range of a few tens of milliseconds.
