Figure 1.
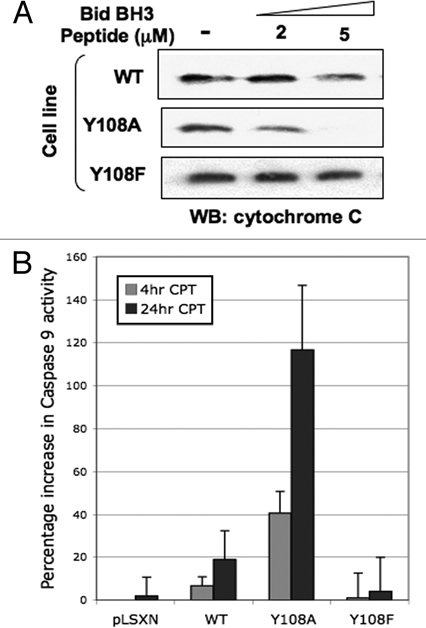
Bak Y108 status plays an important role in determining cytochrome c release from miochondria. (A) Mitochondrial preparations from HCT116 cells expressing either wild type (WT) or Bak mutated at Y108,24 by retroviral transduction (using a pLXSN vector) were incubated with a BH3 peptide derived from Bid than is known to cause cytochrome c release. Mitochondria were then harvested and the remaining cytochrome c levels determined by western blot. Mitochondria isolated from cells expressing the Bak Y108A mutant—that undergoes enhanced conformational change following DNA damage—released more cytochrome c than did WT. Conversely, the Y108F mutant is unable to undergo N-terminal conformational change and is refractory to cytochrome c release by the Bid peptide. (B) HCT116 cells expressing the Bak Y108A mutant showed enhanced activation of caspase 9 at both early and later time points following camptothecin (CPT, 6 µM) treatment than cells expressing WT Bak.
