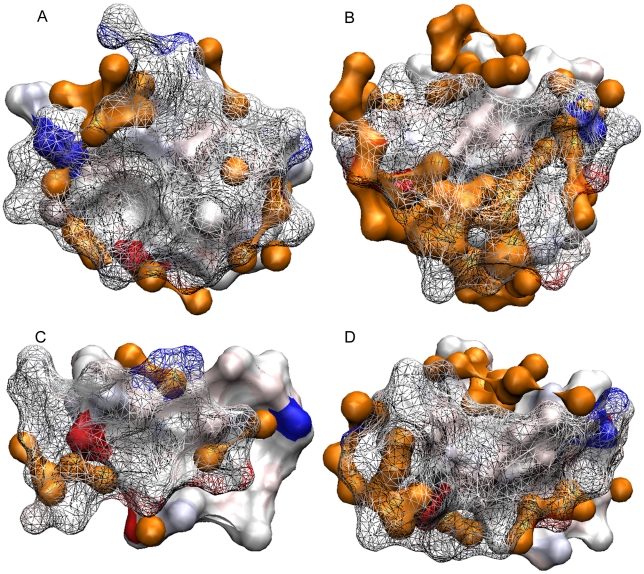
Figure 3. Surface complementarity in the interface of β2—β2 and β4—β4 dimers.
Panel A, β2—β2 interface. Panel B, the β4—β4 found in the orthorhombic crystals. Panel C, the β4—β4 interaction between chains A and B in the tetragonal crystal. Panel D, the β4—β4 interaction between chains C and D in the tetragonal crystal. Atoms pertaining at different chains and within 6.5 Å of each other were represented as a surface. One of the chains was rendered solid and the other as a wire mesh to allow the visibility of the underlying surfaces. Strong blue and red colors were assigned to positively and negatively charged atoms, respectively. Uncharged atoms are depicted accordingly to polarity (pink oxygen, light blue nitrogen, and grey carbon). The surface of water molecules is shown in orange. The page plane bisects the dimers, and the interacting β-strands run horizontally.