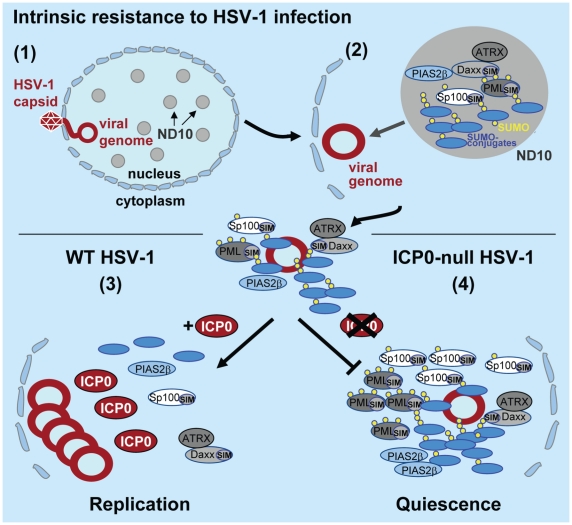
Figure 8. Model depicting the regulation of intrinsic antiviral resistance to HSV-1 infection mediated by the SUMO conjugation pathway.
(1) During the initial stages of HSV-1 infection viral genomes enter the nucleus of infected cells. (2) Major ND10 components including PML, Sp100, hDaxx, and ATRX are recruited into foci that are closely associated with incoming HSV-1 genomes. This recruitment is dependent upon the SUMO conjugation pathway (Figures 1 and S1) and SIMs within PML, Sp100 and hDaxx [17]. (3) During wt HSV-1 infection, the STUbL-like activity of ICP0 promotes the preferential degradation of SUMO-conjugated proteins leading to the dispersal of restriction factors and the efficient onset of viral replication. (4) In the absence of ICP0, specific SUMO-conjugated proteins mediate the transcriptional repression of viral gene expression leading to the establishment of viral quiescence and latency.