Figure 6.
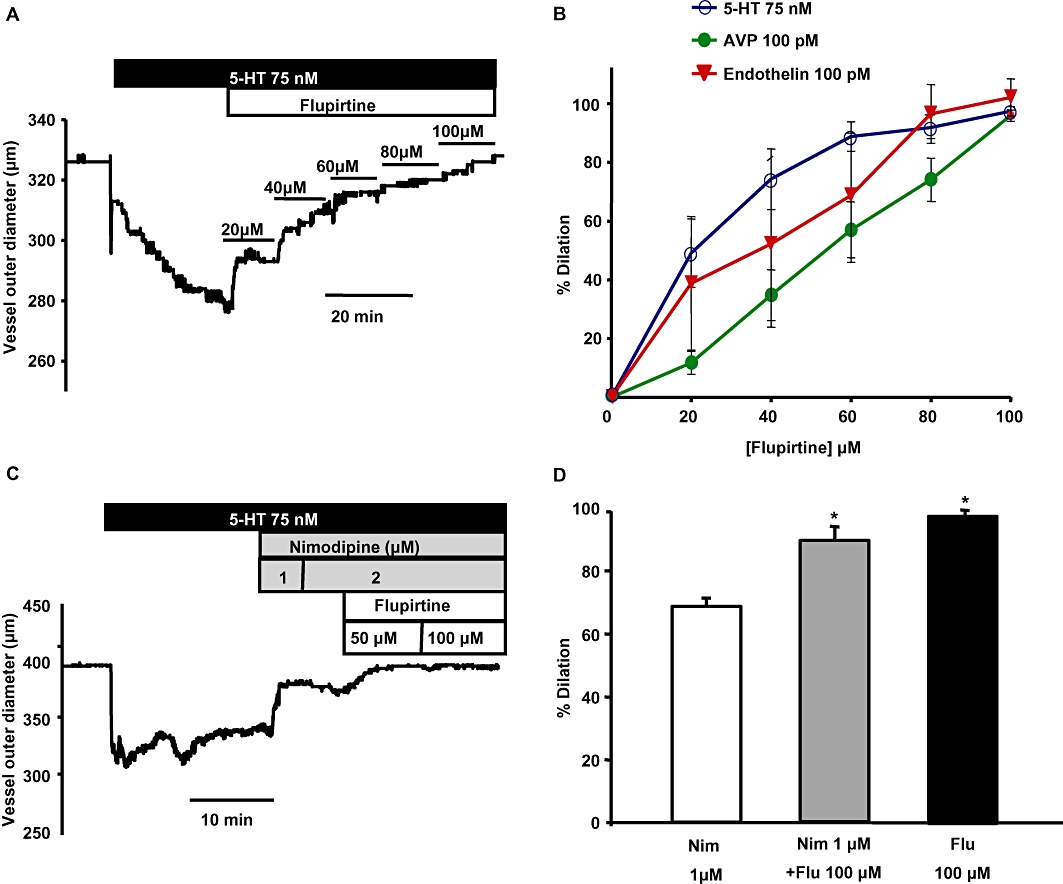
Flupirtine reverses the constriction induced by spasmogens in basilar artery. (A) Representative trace shows the concentration-dependent effect of flupirtine on a basilar artery segment pre-constricted with 75 nM 5-HT. (B) Mean concentration-response curves of the percentage relaxation produced by flupirtine in arteries pre-constricted with the spasmogens: 5-HT, AVP and ET-1. (C) Representative time course trace shows the dilation produced by nimodipine and flupirtine when an artery was pre-constricted with 5-HT. Increasing the concentration of nimodipine above 1 µM did not produce additional dilation. However, addition of flupirtine produced additional dilation in the same artery. (D) Summary of the percentage dilation of basilar artery with the application of 2 µM nimodipine alone, 2 µM nimodipine + 100 µM flupirtine and 100 µM flupirtine alone. Flupirtine either alone or when added along with nimodipine produced significantly more dilation compared with nimodipine alone (n = 3–6 *P < 0.05, one-way anova followed by post hoc Holm-Sidak test).
