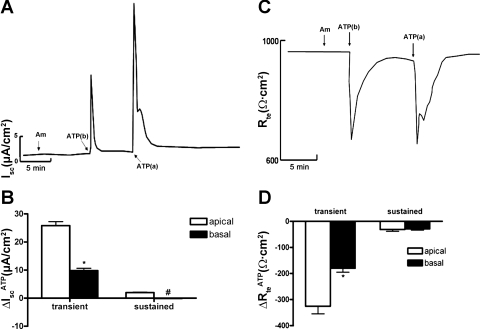
Fig. 1.
Sidedness of ATP-induced short-circuit current (Isc) in inner medullary collecting duct (mIMCD)-K2 cells. A: representative trace of Isc; Am indicates 10−5 M amiloride added to the apical bath; ATP(b) indicates 10−5 M ATP added to the basal side; ATP(a) indicates 10−5 M ATP added to the apical side. B: average Isc values in response to ATP addition (ΔIscATP) to the apical (open bars) or the basal (closed bars) sides. IscATP are categorized as transient or subsequent sustained responses. Values are represented as means ± SE (n = 42 filters). *, #Values significantly different from those induced by ATP added to the opposite side. C: representative trace of transepithelial resistance (Rte); Am indicates 10−5 M amiloride added to the apical bath; ATP(b) indicates 10−5 M ATP added to the basal side; ATP(a) indicates 10−5 M ATP added to the apical side. D: average changes in Rte values in response to ATP addition (ΔRteATP) to the apical (open bars) or the basal (closed bars) sides. ΔRteATP are categorized as transient or subsequent sustained responses. Values are represented as means ± SE (n = 48 filters). *Value significantly different from that induced by ATP added to the opposite side.