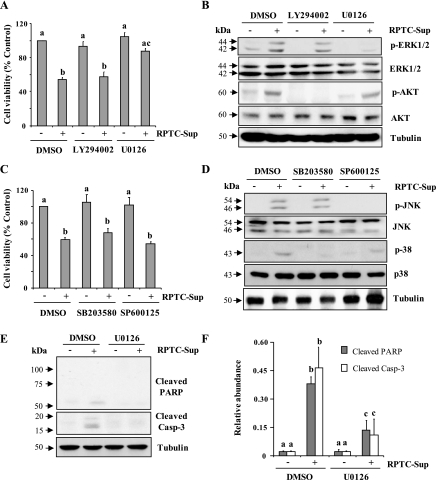
Fig. 3.
Effect of inhibition of ERK1/2, AKT, p38, and JNK on necrotic RPTC-induced renal fibroblast cell death. NRK-49F cells were pretreated with LY294002 (20 μM), U0126 (20 μM), SP600125 (10 μM), or SB 203580 (10 μM) for 1 h and then incubated with necrotic RPTC supernatant for 24 h (A, C, E) or 30 min (B and D). Cell viability was determined by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay (A and B). Values are means ± SD of 3 independent experiments conducted in triplicates and expressed as the percentage of control. Bars with different letters (a–c) are significantly different from one another (P < 0.05). B and D: cells were harvested and cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with specific antibodies against p-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, p- AKT, AKT, p-p38, p38, p-JNK, JNK, or α-tubulin. E: NRK-49F cells were treated with necrotic RPTC supernatant for 24 h in the presence or absence of U0126 (20 μM) and then cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis for active poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase (PARP), active caspase-3, or α-tubulin. The level of cleaved PARP and cleaved caspase-3 was quantified by densitometry analysis and normalized with α-tubulin (F). Data are represented as means ± SD. Bars with different superscript letters (a–c) are significantly different from one another (P < 0.05). Representative immunoblots from 3 experiments are shown.