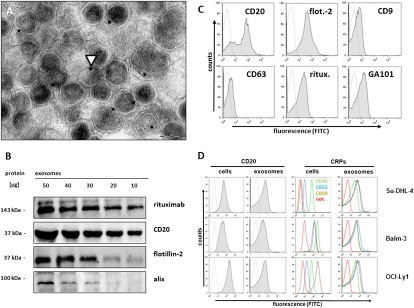
Fig. 1.
Binding of therapeutic anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody to exosomes from B-cell lymphoma cells. (A) Differential ultracentrifugation of cell culture supernatants from B-cell lymphoma cell line Balm-3 yielded microvesicular structures with the typical size and morphology of exosomes staining positive with anti-CD20 antibody rituximab and labeled with protein A–immunogold. Arrowhead indicates immunogold staining. (Scale bar, 100 nm.) (B) Western blot documented binding of rituximab to exosomal protein preparations, detected with an anti-idiotype monoclonal antibody against rituximab (MB2A4), in parallel to CD20 and exosome markers alix and flotillin-2 (Fig. S2 A and B). Binding of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies rituximab and GA101, as well as CD20, flotillin-2 (flot.-2 in C), CD63, and CD9 was also documented by FACS on purified exosome-labeled beads (Su-DHL-4 in C) (cell lines Balm3, OCI-Ly1 in Fig. S2 C and D; and primary lymphoma in Figs. S1G). (D) For the detection of complement regulatory proteins (CRPs), cells or exosomes coupled to beads were stained with fluorescence-labeled monoclonal antibodies and analyzed by flow cytometry. Expression of CD20 (Left panels), as well as of CRPs [Right panels: CD46, green line; CD55, blue line; CD59, brown line; isotype (isot.) control, red line] differed among lymphoma cell lines, whereas levels of CRPs on the exosome surface were uniformly high.