Fig. 1.
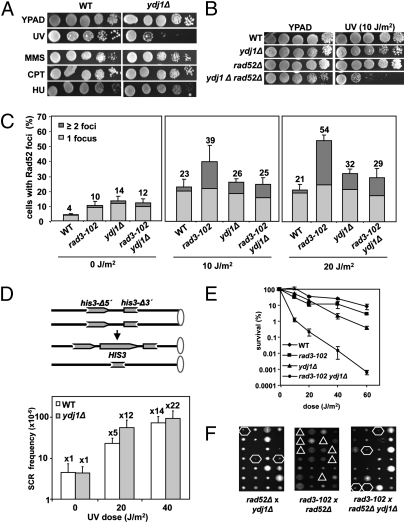
ydj1Δ cells are defective in NER. (A) Tenfold serial dilution assays to establish sensitivity to various DNA damaging agents. Doses used are 60 J/m2 UV, 0.01% MMS, 10 μg/mL CPT, and 50 mM HU. At the indicated doses of MMS, CPT, and HU, the positive control rad51Δ is dead (Fig. S1D). (B) Tenfold serial dilution assays to measure UV sensitivity at a 10-J/m2 dose in ydj1Δ cells in the absence of Rad52. (C) Spontaneous and UV-induced accumulation of Rad52 foci in WT, ydj1Δ, rad3-102, and their corresponding double mutant cells in S and G2 carrying the RAD52-YFP construct with or without UV irradiation. (D) Recombination frequency in response to UV in the direct-repeat system his3- Δ5′- his3-Δ3′, which measures unequal sister chromatid exchange in WT and ydj1Δ cells. Mean and SD of three independent fluctuation tests were calculated for each genotype. (E) Survival curves after UV irradiation of ydj1Δ, rad3-102, and their corresponding double mutant. (F) Tetrad dissection of crosses to obtain double mutants ydj1Δ rad3-102, rad52Δ rad3-102, and the triple mutant ydj1Δ rad52Δ rad3-102. Hexagons indicate viable combinations and triangles lethal combinations.