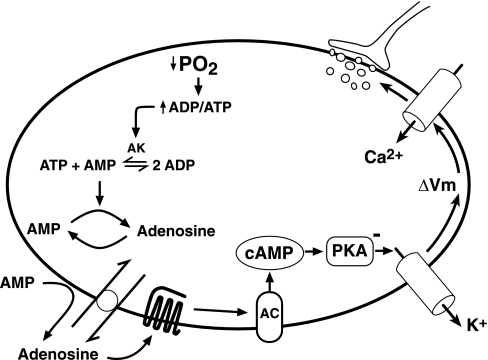
Fig. 3.
Adenosine A2A receptor transduction cascade proposed for carotid body activation. O2-limitation of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria activates adenylate kinase (AK), which converts two molecules of ADP into ATP and AMP. The resulting increase in the AMP/ATP ratio promotes adenosine formation from AMP in cytosol and extracellular space. Intracellular adenosine is transported extracellularly via an equilibrative nucleoside transporter. Activation of extracellular A2A receptors stimulates cAMP formation by adenylyl cyclase (AC), which, in turn, promotes protein kinase A (PKA) inhibition of potassium currents. The resulting fall in membrane potential (ΔVm) activates voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, and the rise in intracellular Ca2+ leads to secretion of neurotransmitters that stimulate the carotid sinus nerve.