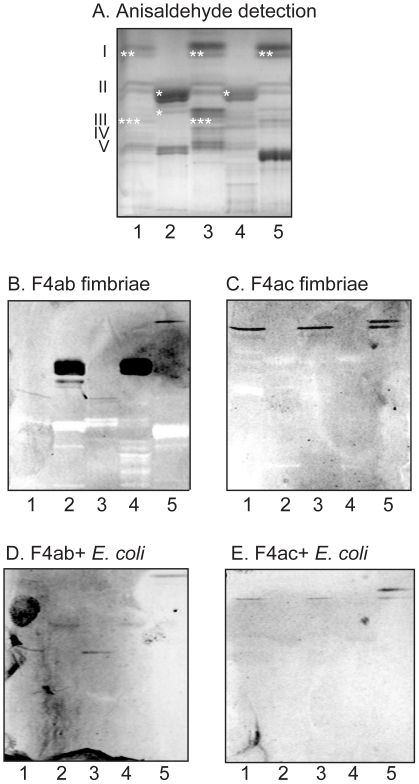
Figure 6. Binding of F4ab and F4ac fimbriae, and F4ab- and F4ac-fimbriated Escherichia coli, to mixtures of glycosphingolipids from porcine intestinal mucosa.
Chemical detection by anisaldehyde (A), and autoradiograms obtained by binding of F4ab fimbriae (B), F4ac fimbriae (C), F4ab-expressing E. coli (D), and F4ac-expressing E. coli (E). The lanes were: Lane 1, non-acid glycosphingolipids of 3-day old piglet small intestinal mucosa, 40 µg; Lane 2, acid glycosphingolipids of 3-day old piglet small intestinal mucosa, 20 µg; Lane 3, non-acid glycosphingolipids of adult pig 1 small intestinal mucosa, 40 µg; Lane 4, acid glycosphingolipids of adult pig 1 small intestinal mucosa, 40 µg; Lane 5, non-acid glycosphingolipids of adult pig 2 small intestinal mucosa, 40 µg. The Roman numbers to the left of panel A indicate the approximate number of carbohydrate residues in the bands in the non-acid fractions (lanes 1, 3 and 5). The approximate migration level of the F4ab-/F4ac-binding compounds have been marked with *, **, and *** in panel A.