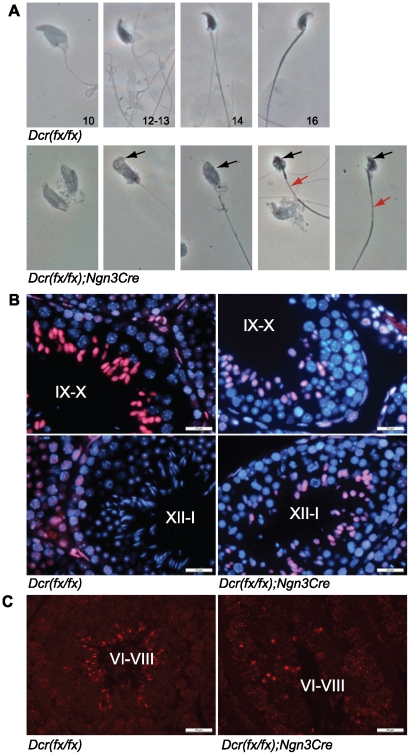
Figure 4. Defects in late spermiogenesis.
A) Phase contrast microscopy of spermatogenic cells revealed defects in elongating spermatids. Knockout elongating spermatids had malformed head shape and abnormal chromatin condensation (black arrows). Formation of the flagellum was also affected. Red arrows point to the disorganized midpiece in elongating spermatids. B) Immunofluorescence of PFA-fixed testis sections with anti-acetylated-H3 antibody (red). Knockout tubules showed strong hyperacetylation of H3 in step 9–10 spermatids, but the signal was retained in later stages most probably indicating an arrest or delay in spermatid elongation. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). C) Immunofluorescence of testis sections with anti-PRM1 antibody (red) demonstrated the decreased number of protamine-containing elongating spermatids in knockout tubules. Scale bar: 25 µm.