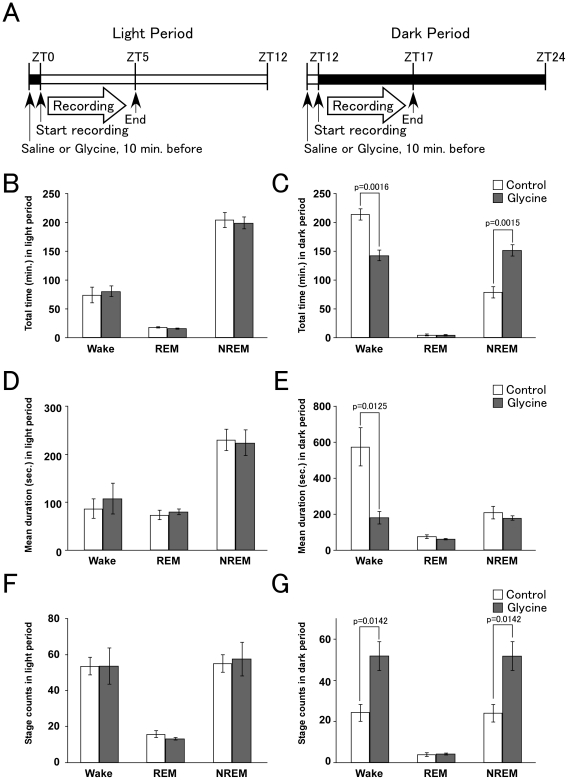
Figure 1. Glycine-induced sleep phenotype during dark period.
A Protocols for glycine administration in light (left panel) or dark period (right panel). Glycine or saline was injected intraperitoneally 10 min before the start of recording (ZT0 or ZT12). EEG/EMG recordings were performed for the next 5 hours (until ZT5 or ZT17). B, C Total time (minutes, mean ± SEM) spent in each state in saline- (n = 4, white bar) and glycine-administered mice (n = 4, gray bar), itemized separately for light (B) and dark periods (C). D, E Episode duration (seconds, mean ± SEM) spent in each state in saline- and glycine-administered mice, in light (D) or dark period (E). F, G Stage count (count, mean ± SEM) is number of each episode during each period (light; F, dark; G). The glycine-administered group showed a significantly shorter total time and duration of episodes of wakefulness, suggesting fragmentation of sleep/wakefulness states during the dark period. *p<0.015. Graphs summarize the data recorded during the 5 h light/dark period.