Figure 1. PKCδ inhibition promotes endothelial barrier dysfunction.
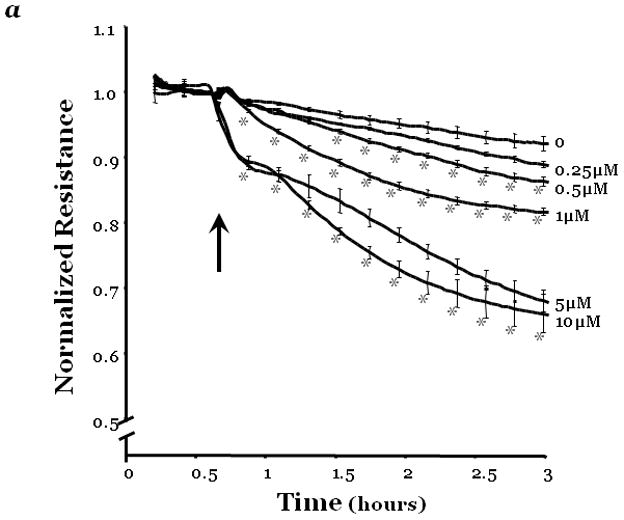
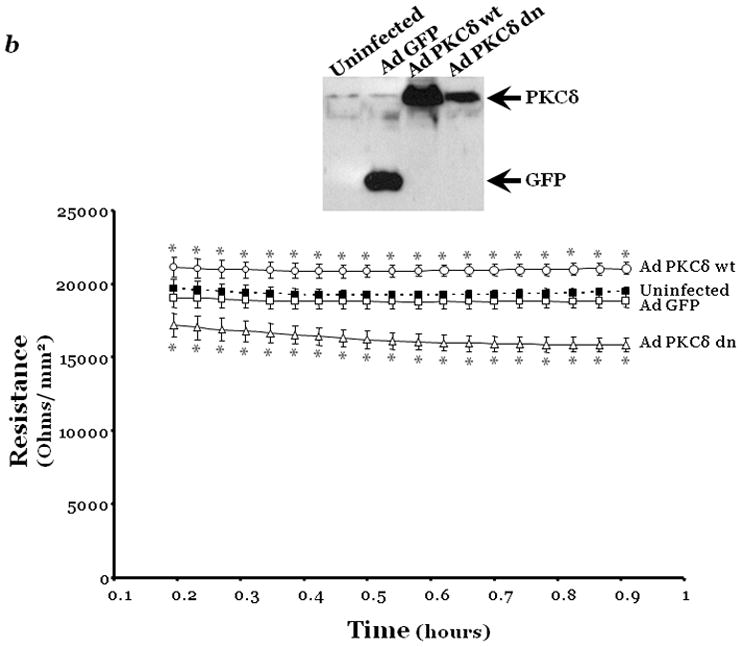
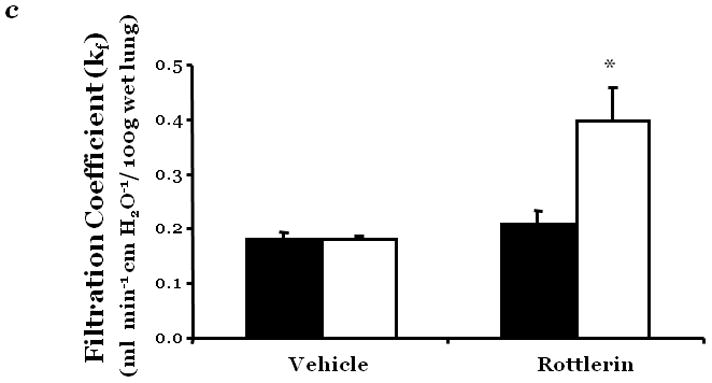
Changes in endothelial monolayer permeability were assessed in rat lung microvascular endothelial cells (LMVEC) (panel a) or endothelial cells derived from the epididymal fat pad (FPEC) (panel b) by assaying changes in resistance of endothelial monolayers grown on collagen coated gold electrodes using the electrical cell impedance system (ECIS); a drop in electrical resistance across the endothelial monolayers correlates with increased permeability. Panel a, vehicle (DMSO) or indicated concentration of rottlerin (a chemical inhibitor with specificity for PKCδ, relative to other PKC isoforms) was added to the monolayers, with arrows indicating time of addition. Panel b, endothelial monolayers containing equivalent numbers of endothelial cells were infected with indicated adenovirus. Protein overexpression was confirmed by immunoblot analyses (inset) and the effect of the overexpressed protein on monolayer permeability was determined by measuring the electrical resistance across the monolayers 24 hours post-infection. The mean±SE of the normalized electrical resistance are presented. Panels a, n=6–12; *p<0.05 vs. vehicle. Panel b, n=16; *p<0.05 vs. Ad GFP or uninfected. Panel c, pulmonary vascular permeability was measured by calculating the capillary filtration coefficients (Kf), using the Starling equation, from isolated, perfused rat lungs, which were fully recruited and in an isogravametric state. Kf was determined by measuring the lung weight gain following an increase in venous pressure divided by the change in capillary pressures and normalized to 100g wet lung mass at baseline (solid bars) and following a 45 minute exposure to vehicle (DMSO) or 50μM rottlerin (open bars). n=3–4, *p<0.05.
Panels a, c, and d: Reprinted from Klinger, J.R., et al., 2007. Rottlerin causes pulmonary edema in vivo: A possible role for PKCδ. Journal of Applied Physiology, 103:2084–2094. Panel b: Reprinted from Harrington, E.O., et al., 2005. PKCδ regulates endothelial basal barrier function through modulation of RhoA GTPase activity. Experimental Cell Research, 308:407–421.
