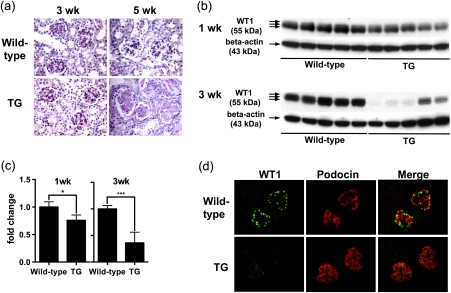
Fig. 5.
WT1 protein expression is reduced in podocytes in Alb/TGF-beta1 transgenic mice. (a) Representative Periodic acid-Schiff stained kidney sections were obtained from wild-type or Alb/TGF-beta1 transgenic (TG) mice at 3 and 5 weeks of age. At 3 weeks of age, WT and transgenic mice glomeruli showed no pathologic changes. At 5 weeks of age, transgenic mice showed moderate-to-severe diffuse global glomerulosclerosis characterized by mesangial matrix expansion and occlusion of the glomerular capillary tuft. Original magnification, x400. (b) WT1 protein expression in whole kidney lysates of wild-type or TG mice at 1 or 3 weeks of age was analyzed by western blotting. The triple bands indicate the presence of WT1 splice variants. (c) The intensity of bands in panel (b) was quantitated by densitometry and normalized to beta-actin protein. WT1 protein expression was significantly reduced in transgenic mice compared with wild-type mice at both 1 and 3 weeks of age, although the difference was modest at 1 week. For each age, relative mean ± SD values are shown, normalized to values for wild-type mice. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. (d) Kidney sections of 3-week-old wild-type or transgenic mice were subjected to double immunostaining for WT1 and podocin. WT1 (green) is located in the nuclei of glomerular cells that also expressed podocin in the cytoplasm (red) in wild-type mice kidneys. WT1 expression was attenuated in transgenic mice kidneys, while podocin expression was retained. Original magnification, x400.