Figure 6.
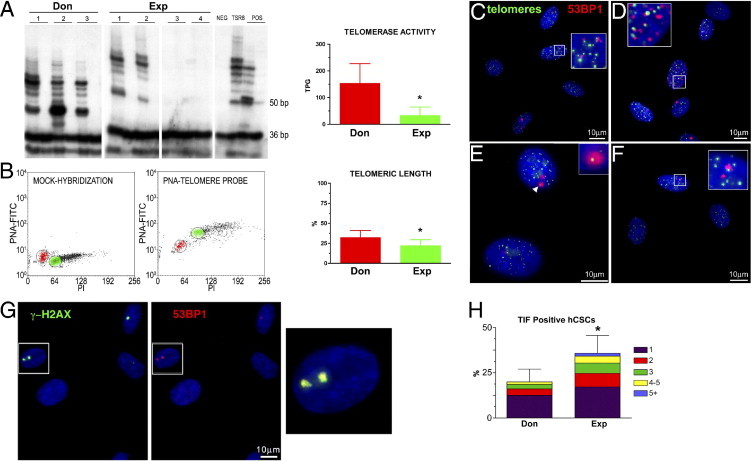
Telomere-telomerase axis in hCSCs from donor (Don) and explanted (Exp) hearts. A: In hCSC classes, products of telomerase activity display a 6-bp periodicity. Heat-inactivated lysates were used as negative control (lane 2 for each sample). TSR8 indicates telomerase control template; the 1301 cell line was used as a positive control (POS), and the primer-dimer lane as negative control (NEG). B: Dot plots of hCSCs hybridized without (mock-hybridization) and with the peptide nucleic acid (PNA) telomere probe. Gates were set around cells in the G0/G1 phase for both hCSCs (red) and control cells, tetraploid 1301 cell line (green). PI, propidium iodide. Relative telomeric length was computed as the ratio of the telomere signal of hCSCs and control cells. C–F: Four examples of telomere dysfunction-induced foci (TIFs) in which 53PB1 (red) colocalizes with telomere hybridization spots (green). Detail of interest (arrowhead, inset) is shown at higher magnification in the corresponding inset. G: γ-H2AX (green) and 53BP1 (red) colocalize at sites of DNA damage. The area included in the rectangles is shown at higher magnification on the right (yellow merged signals). In histograms, data are reported as means ± SD. H: Fraction of hCSCs with 1 to 5 TIFs. *P < 0.05 versus Don. Scale bars: 10 μm.
