Figure 6.
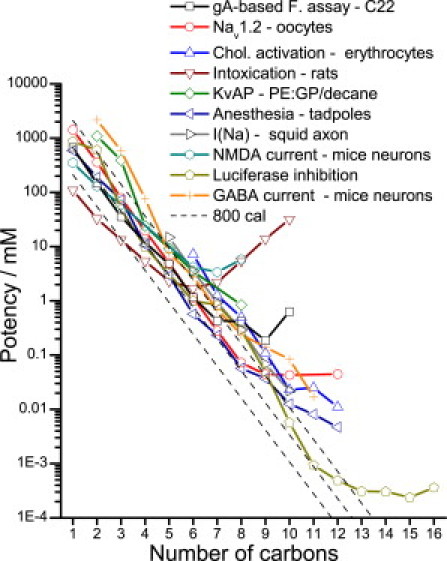
Potency of straight-chain alcohols in different systems. An alcohol's potency is defined differently depending on the system, as follows: D for the gA-based fluorescence assay in DC22:1PC lipid vesicles (boxes); IC50 inhibition of Nav1.2 sodium current in oocytes (65) (circles); cholesterol activation measured as the concentration that promotes hemolysis of red blood cells in a cholesterol oxidase assay (66) (up triangles); ED3 is the injected dose required (in mmole/kg, not mM) to produce ataxia 2 behavior (as described by Majchrowicz (67)) for intoxication in rats (56) (down triangles); IC67% reduction in unitary conductance of KvAP channels reconstituted in PE:GP/n-decane planar bilayers (23) (diamonds); anesthesia ED50 as determined by the loss of righting reflex of tadpoles (68) (left triangles); 50% suppression of peak inward current in voltage-clamped intact giant squid axons (69) (right triangles); EC50 inhibition of NMDA-induced current in mice hippocampus neurons (70) (hexagons); ED50 50% reduction of luciferase fluorescence in buffer (27) (pentagons); and EC50 potentiation of GABA-induced current in mice hippocampus neurons (71) (crosses). The dashed lines have slopes of 0.59 log units representing 800 cal/mole per –CH2 group.
