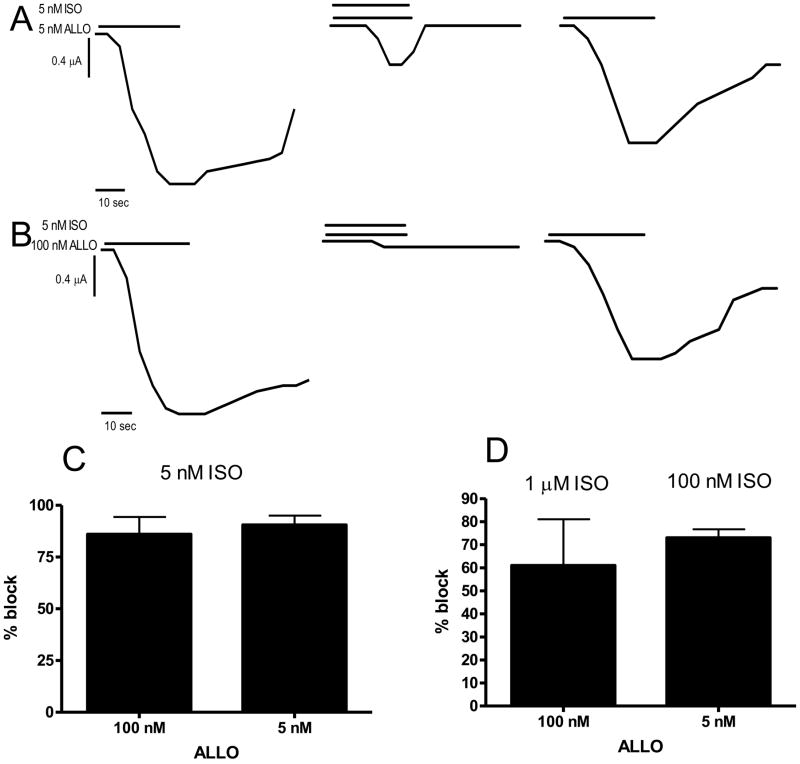
Figure 4.
ISO inhibits ALLO induced currents α1S299C containing receptors. A: 5 nM ALLO induces significant current at α1S299C containing receptors (first trace). That current is blocked by 5 nM ISO (second trace) but is mostly recovered after the ISO is washed out and 5 nM ALLO reapplied (third trace). Representative of 3 experiments. 100 nM ISO blocked current induced by 5 nM ALLO similarly (not shown). B: 100 nM ALLO induces significant current at α1S299C containing receptors (first trace). That current is blocked by 5 nM PTN (second trace) but is recovered after the ISO is washed out and 100 nM ALLO reapplied (third trace). Representative of 3 experiments. 1 μM ISO blocked current induced by 100 nM ALLO similarly (not shown). C: Bar graph of 5 nM ISO blocks on simultaneously added 100 nM or 5 nM ALLO on α1S299C containing receptors. 5 nM ISO inhibits both 100 nM and 5 nM ALLO induced currents 80–85%. All sample number of 3. D. Bar graph of 1 μM ISO block on simultaneously added 100 nM ALLO and 100 nM ISO block of 5 nM ALLO on α1S299C containing receptors. 1 μM ISO inhibits 100 nM ALLO currents about 60% and 100 nM ISO blocks 5 nM ALLO induced currents 90%. All sample number of 3.