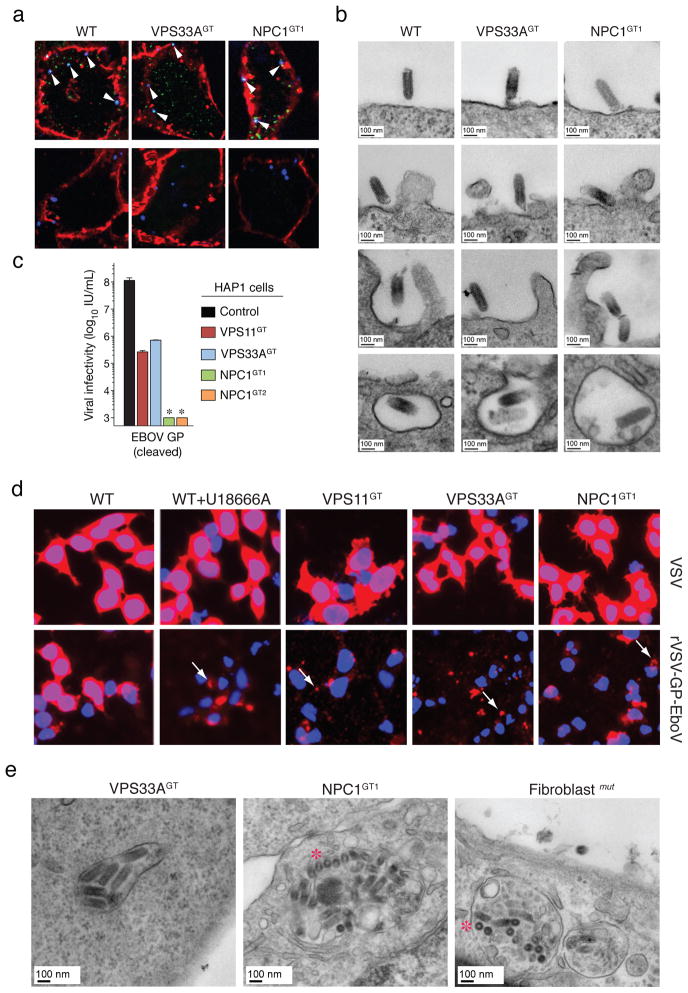
Figure 3. Ebola virus entry is arrested at a late step in cells deficient for the HOPS complex and NPC1.
a, Viral particles attach and internalize into HOPS-and NPC1-deficient cells. Indicated HAP1 clones were infected with Alexa 647-labeled rVSV-GP-EboV (blue) at 4°C. Non-internalized, bound viral particles (blue) were also stained with a GP-specific antibody (green) and the plasma membrane with Alexa 594-wheat germ agglutinin (red) (top panels). To assess viral internalization, cells were warmed to 37°C (bottom panels). Internalized viral particles (blue punctae) are resistant to acid-stripping and inaccessible to a GP antibody. b, Cells were inoculated with rVSV-GP-EboV and examined by transmission electron microscopy. Representative images of early entry steps are shown. c, In vitro-cleaved rVSV-GP-EboV cannot bypass the infection block observed in VPS11GT, VPS33AGT and NPC1GT cells. Infectivity of thermolysin-cleaved rVSV-GP-EboV in the indicated HAP1 clones. *below the limit of detection. d, Viral escape into the cytoplasm is blocked in HOPS complex- and NPC1-deficient cells. Wild type HAP1 cells treated with U18666A (10 μg/ml), and the indicated mutant clones were infected with VSV or rVSV-GP-EboV virus for 3h and processed for VSV M staining (red). Punctuate staining is indicated by arrows. e, Electron micrographs of rVSV-GP-EboV-infected VPS33A- and NPC1-deficient HAP1 cells and NPC1-deficient fibroblasts showing agglomerations of bullet-shaped VSV particles in vesicular compartments. All images were taken at 3 h post-inoculation. Asterisks highlight rVSV-GP-EboV particles in cross-section.