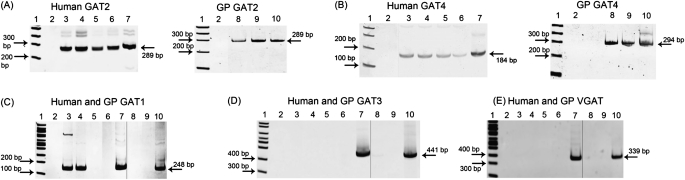
Figure 1.
Representative gel images of RT-PCR of γ–amino butyric acid (GABA) transporter (GAT) subtypes from RNA from freshly dissected human and guinea pig (GP) tissues and cultured human airway smooth muscle (ASM) and epithelial cells. mRNA for (A) GAT2 and (B) GAT4 is present in native human ASM and epithelium, cultured human ASM and epithelium (A and B, left panels), and native guinea pig ASM and epithelium (A and B, right panels). (C) mRNA for GAT1 is present in native human ASM and epithelium, and may represent contaminating neural structures in these tissues. mRNA for (D) GAT3 and (E) vesicular GAT (VGAT) is not present in human or guinea pig ASM or epithelium. Images are representative of experiments performed on RNA isolated from two to three different native guinea pig or human tissues, or two to three cultured cell flasks. 1, 100 base pair ladder; 2, water, which denotes the negative control (no cDNA input); 3, native human ASM tissue; 4, native human airway epithelial tissue; 5, cultured human ASM cells; 6, cultured human airway epithelial cells; 7, human brain; 8, native guinea pig ASM tissue; 9, native guinea pig airway epithelial tissue; and 10, guinea pig brain. Separate gel images are denoted by a solid demarcating line.