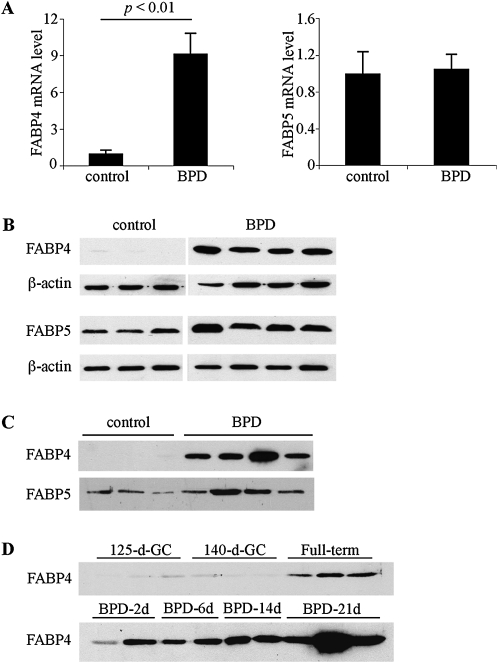
Figure 1.
The expression of fatty acid–binding protein 4 (FABP4) is increased in bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). (A) Real-time RT-PCR for FABP4 and FABP5 was performed on total lung RNA, isolated from control and BPD group baboons (n = 6–7 samples per group). Relative expression levels were normalized to β-actin by the 2−ΔΔCT method. An arbitrary level of 1 was assigned to the control group. (B) FABP4 and FABP5 protein expression in whole baboon lung homogenates was analyzed by immunoblotting. β-actin was used as a loading control. (C) FABP4 and FABP5 were detected by immunoblotting in necropsy bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). (D) Time course of FABP4 detection in necropsy BALF samples.