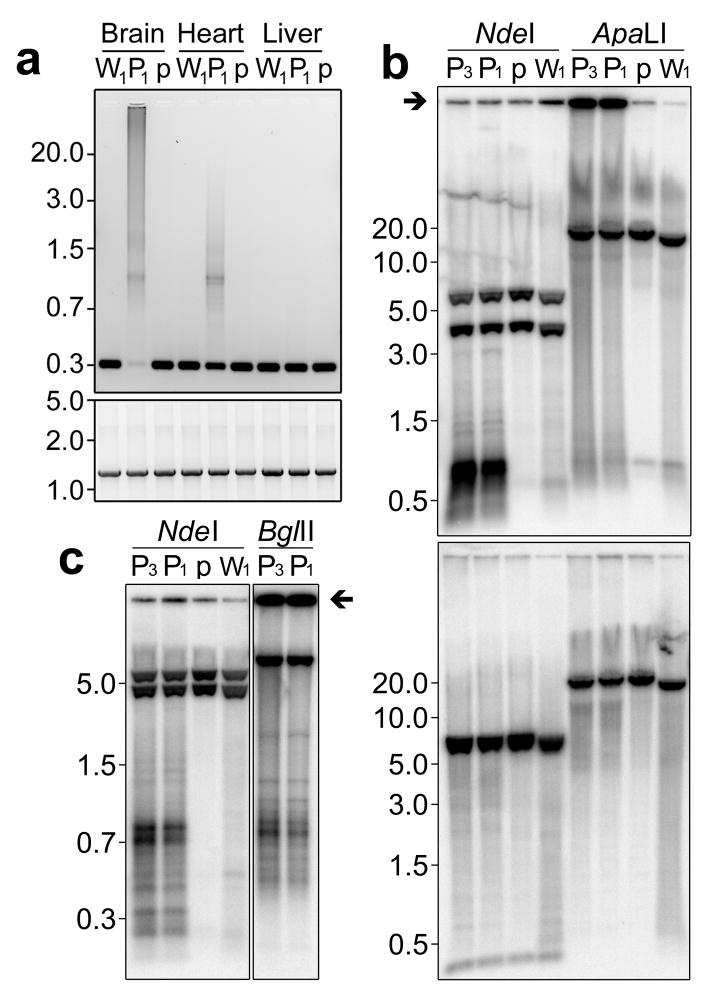
Figure 4. Probing CRM structure using PCR and Southern blotting.
(a) Resolution of long-extension PCR products amplified using PCR primers within the CRM region (upper panel) and outside of it (lower panel) using DNA from brain, heart and liver of Polgwt/wt (W1), PolgD257A/D257A (P1) and PolgD257A/wt (p) mice. (b) Southern blots of total DNA from brain of mice described in panel (a) with an additional PolgD257A/D257A sample (P3). DNA was digested with NdeI or ApaLI and hybridized with a probe against the control region (upper panel) or an alternate probe against nt8,926 – 10,081 (lower panel). (c) Resolution of CRMs using high percentage agarose gels following NdeI or BglII digestion. Immobile control region signal is indicated with arrows in panels b and c. NdeI cleaves wild-type mtDNA at 5 sites. The control region probe binds wild-type NdeI fragments of 5.9 and 3.8 Kb and the alternate probe binds NdeI fragments of 6.3, 5.9 and 0.2 Kb.