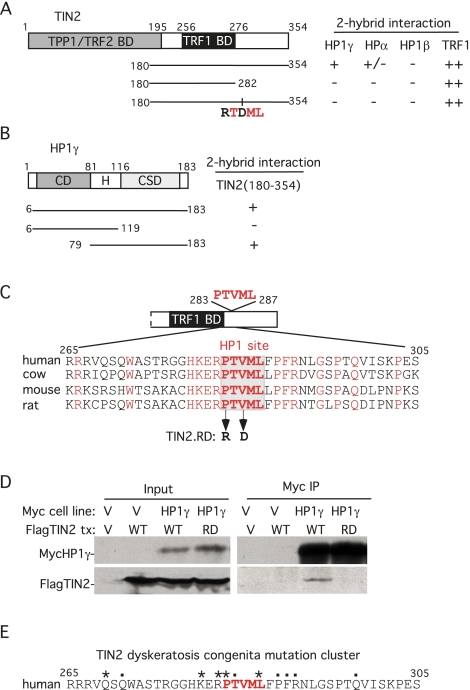
Figure 1.
HP1 binds to the PTVML site in the DC-associated TIN2 mutation cluster. (A) Schematic representation of TIN2 and two-hybrid interaction with HP1. TPP1-, TRF2-, and TRF1-binding domains (BDs) and the double point mutation in TIN2 (RTDML) are indicated. (B) Schematic representation of HP1 and two-hybrid interaction with TIN2. The chromodomain (CD), hinge (H), and chromoshadow domain (CSD) in HP1 are indicated. (A,B) Two-hybrid interactions were scored according to the number of minutes required for the color change: 20 min (++), 45 min (+), and 150–180 min (+/−). (C) Alignment of the TIN2 domain containing the PTVML HP1-binding site. Identical amino acids are indicated in red. (D) HP1 binds to TIN2 in human cells. HT1080 stable cell lines expressing HP1γ or vector (V) were transfected with vector or FlagTIN2 (WT or RD). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-myc beads and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-myc or anti-TIN2 701 antibody. (E) The DC-associated mutation cluster in TIN2. DC mutations are indicated by dots and asterisks; asterisks indicate mutations shown to give rise to shortened telomeres.