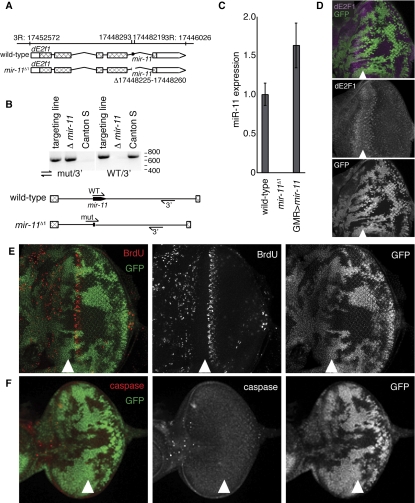
Figure 3.
Generation and initial characterization of mir-11 mutant. (A) Genomic organization of the mir-11 region. (B) Genomic DNA was extracted from wild type (Canton S); the targeting line used for homologous recombination, which contains wild-type and mir-11 mutant intron sequences (targeting line); or the homozygous mir-11 mutant (Δ mir-11) flies. PCR was performed using primers binding to the regions indicated to follow the presence and loss of the mir-11 gene. (C) RNA was extracted from wild-type (Canton S), mir-11 mutant, or GMR>mir-11 larvae. The dme-miR-11 TaqMan assay was used to measure mature miR-11 expression. (D–F) Clones of mir-11 mutant tissue were generated using ey-FLP. Wild-type tissue is marked by GFP (green). (D) Third instar larval eye discs were dissected, and dE2F1 expression (magenta) was detected by immunofluorescence. (E) To mark proliferating cells, eye discs were incubated with BrdU for 60 min prior to fixation and antibody staining. (F) Apoptotic cells were labeled with the C3 antibody, which recognizes the active forms of caspases.