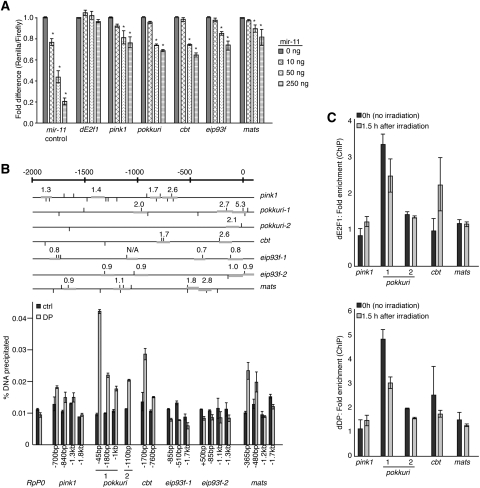
Figure 7.
miR-11 and dE2F1 directly regulate a common set of genes involved in the regulation of cell death. (A) 3′ UTR sensor assays were performed in HeLa cells using control or dE2F1/miR-11 shared targets identified by bioinformatic prediction algorithms. Fifty nanograms of the indicated 3′ UTR sensor plasmid was transfected with the indicated amounts of pcDNA3/empty or pcDNA3/mir-11 plasmids. Cells were harvested 40–48 h post-transfection, and luciferase assay was measured. Error bars represent the standard deviation. A minimum of three independent transfections was performed for each sensor construct. (*) P < 0.05 in a paired t-test compared with 0 ng pcDNA3/mir-11. (B) Schematics of promoter regions (−2 kb to +100 bp relative to transcription start site) of predicted targets of both miR-11 and dE2F1. RSAT binding site analysis was performed using the NWTSSCSS consensus E2F-binding site (van Helden 2003). Predicted binding sites are shown as vertical lines above and below promoter region, representing forward and reverse binding site orientation, respectively. Thick gray horizontal bars represent PCR products from primers tested in ChIP. Numbers above PCR products indicate fold enrichment from ChIP with DP antibody versus ChIP with nonspecific antibody. ChIP from S2R+ cells using a dDP or nonspecific control antibody (ctrl). Real-time qPCR analysis was done on the recovered chromatin samples, and the total amount of DNA precipitated with each antibody was quantified. RpP0 served as a negative control. Error bars represent the standard deviation from the mean. (C) S2R+ cells were exposed to 40 Gy of irradiation, and cells were fixed 1.5 h later. The 0-h sample was not exposed to irradiation. Sonicated chromatin was immunoprecipitated with an antibody that recognizes dDP, dE2F1, or an IgG control. The level of enrichment from the DP and dE2F1 antibodies was compared with that from the IgG control, and enrichment values were normalized to the RpP0 gene control.