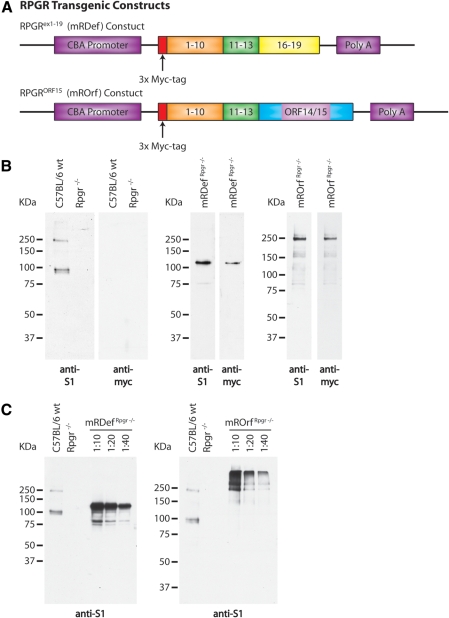
Figure 5.
Schematic illustration of transgenic constructs and confirmation of transgene expression. (A) Top: an Rpgrex1-19 transcript was cloned between the cytomegalovirus (CMV) enhancer β-actin promoter (CBA) and a bovine growth hormone (BGH) polyadenylation sequence. Bottom: a full-length RpgrORF15 transcript was cloned from a combination of genomic and cDNA. Exons 1-13 were cloned from wild-type retinal cDNA and the final exon, ORF14/15, was cloned from genomic cDNA. An N-terminal Myc tag was integrated in both transgenic constructs to allow for differentiation between transgenic and native Rpgr expression. (B) Left: immunoblot analysis of retinal homogenate from wild-type and Rpgr−/− mice using our polyclonal anti-S1 and monoclonal anti-myc antibodies. Middle: verification of transgene expression by immunoblot analysis of retinal homogenate from mRDefRpgr−/− transgenic mice. Right: verification of transgene expression by immunoblot analysis of retinal homogenate from mROrfRpgr−/− transgenic mice. (C) Comparison of transgenic expression levels with Rpgr expression in wild-type retina by immunoblot analysis with the anti-S1 antibody.