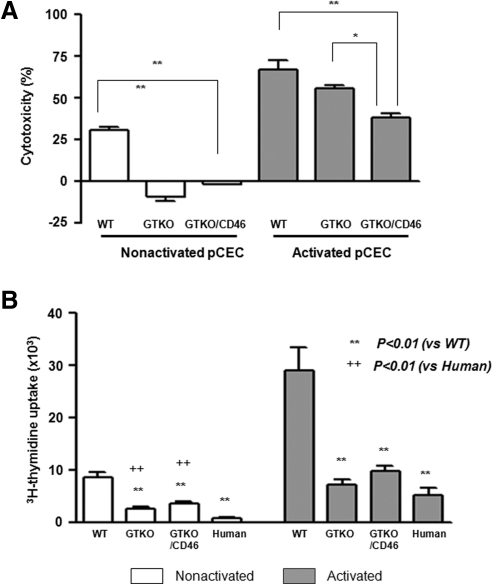
Figure 6.
Significant reduction of the human humoral and cellular responses to genetically engineered pCECs. (A) A complement-dependent cytotoxicity assay showed lysis of the WT, GTKO, and GTKO/CD46 pCECs before and after activation (by pIFN-γ 40ng/mL for 48 hours) by pooled human serum at 12.5% concentration. In contrast to the WT pCECs, there was no lysis of the quiescent GTKO and GTKO/CD46 pCECs. After activation, although there was increased lysis of the pCECs from all types of pig, there was significantly less lysis of the GTKO/CD46 pCECs than of the pCECs from other pigs (n = 4; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (B) Human CD4+ T cells were co-cultured with the WT, GTKO, GTKO/CD46 pig or human stimulator CECs before and after activation for 6 days. MLR showed significantly less proliferation of human CD4+ T cells to GTKO and GTKO/CD46 pCECs and to hCECs than to the WT pCECs. There was significantly less proliferation of human CD4+ T cells to the quiescent hCECs than to the GTKO and GTKO/CD46 pCECs. After activation, however, there was no difference in human CD4+ T-cell proliferation to the GTKO and GTKO/CD46 pCECs or to the hCECs (n = 4; **P < 0.01 vs. WT, ++ P < 0.01 vs. human).